
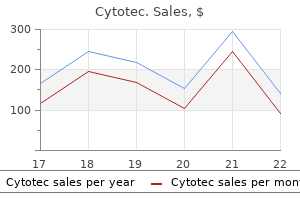
Cytotec dosages: 200 mcg, 100 mcg
Cytotec packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Generic cytotec 100 mcg line
There treatment 4 pimples cytotec 200 mcg discount otc, either most or all the drainage from the higher lobe symptoms 8 weeks 200 mcg cytotec sale, after passing through the bronchopulmonary (hilar) lymph nodes, moves either by the use of the tracheobronchial and tracheal (paratracheal) lymph nodes, bronchomediastinal trunk, scalene nodes, and thoracic duct to the brachiocephalic vein or by means of the aortic arch nodes to the same termination. From the left decrease lobe and often from the lingula, lymph flows to the best after passing by way of the bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes and goes largely to the decrease tracheobronchial (carinal) lymph nodes. It then follows the identical course because the lymph from the right lung by the use of the right tracheal (paratracheal) nodes-an essential point in illness, particularly tumors of the left lower lobe. Finally, there are probably cross-connections between the proper and left tracheal (paratracheal) nodes, a scenario which will further alter the drainage pathways. This classification is anatomically primarily based and validated, permitting for consistent lymph node mapping utilized in staging lung cancer. Protecting the respiratory system from pathogens and toxins while avoiding pointless inflammation when harmless proteins are inhaled is a challenge. Ingestion of organisms and particulate material by macrophages resident throughout the lung is another essential line of defense. Ingestion of silica particles or asbestos fibers by macrophages may fail to clear these particles and may lead to persistence of inflammation and in the end lung tissue harm. Activated epithelium secretes chemoattractant molecules that will appeal to neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes, relying on the particular need. Defensins are proteins that are secreted by epithelial cells which will bind to microbial cell membranes and create pores that assist in killing organisms. Indeed, the epithelial cells are the first target for a selection of respiratory viruses similar to rhinovirus and adenovirus. These cells recirculate and may home to the site of origin of the dendritic cell, the place they could now produce cytokines that play a key function in directing the sort of inflammation. Whereas Th1 kind cells are related to delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, Th2 cells may lead to typical eosinophil-rich Physical obstacles filter out giant particles in the nose Adaptive response 1. T-cells are activated, proliferate, and return to bronchial mucosa Foreign particle four. Regulatory T cells could forestall, restrict, or participate in terminating inflammation. Other newly described T-cell subsets similar to Th17 cells are associated with inflammation that has a powerful neutrophilic component, and these cells could additionally be implicated in additional severe forms of bronchial asthma. In the change from an aqueous to an cardio environment, many fundamental buildings have been modified however retained as components of the respiratory system, and others became nonrespiratory constructions. The olfactory organ of aqueous types was included into the respiratory system of terrestrial forms, and the easy sphincter mechanism of the swim bladder of fish grew to become the larynx of air breathers, which additionally took on the function of phonation. By and in the course of the eighth gestational week, the rudiments of the sixteen to 20 C-shaped tracheal cartilages seem (see Plate 1-36). These buds develop secondary branches to the future lobes: the higher, middle, and lower lobes on the best facet and the upper and lower lobes on the left (Plate 1-34). By the seventh week, tertiary branches appear (see Plate 1-35), 10 in the proper lung and 9 in the left. These tertiary branches will provide the clinically important bronchopulmonary segments, which turn out to be separated from one another by tenuous connective tissue septa (see Plate 1-36). A branch of the pulmonary artery accompanies every segmental bronchus to function the unbiased blood provide to a bronchopulmonary section. At 28 weeks, seven-eighths of the potential grownup number of mucous glands is present in the respiratory tubes. By the third gestational month, smooth muscle cells differentiate to form the posterior wall of the trachea and extrapulmonary primary bronchi, which completely lack cartilage. Because inspiration is affected by contraction of powerful muscles and is related to widening and lengthening of the bronchial tree muscles, individuals with asthma can normally encourage adequately. But these individuals have great problem exhaling as a result of expiration usually results from passive recoil of the stretched thoracic wall and lungs. Normally, each is just a potential space with serous lining that produces a slimy secretion. During the second week of life, the two coelomic cavities in the area of the growing heart fuse right into a single pericardial coelom. Therefore, the two channels of communication between the pericardial coelom and the 2 primitive coelomic cavities persist to turn out to be the pleural canals. Pleural Canals In the fish stage of vertebrate evolution, the transverse septum utterly separates the pericardial and peritoneal cavities. Pleuropericardial and Pleuroperitoneal Folds the vertically oriented pleuropericardial folds come up on each side from the physique partitions where the common cardinal veins swing round to enter the sinus venosus, which subsequently turns into the best atrium. These body-wall folds bulge into the pleural canals between the lungs and the guts (see Plates 1-34 and 1-38). At this time, the latter space contains the lungs in addition to the abdominal and pelvic viscera. Reptiles have a twin muscular respiratory mechanism: the motion of the trunk muscle tissue creates adverse strain, and the ground of the mouth pushes air into the lungs beneath positive strain. The diaphragmatic striated musculature migrates to the transverse septum together with branches of the third, fourth, and fifth cervical spinal nerves, which become its unique motor nerve by way of the phrenic nerve. As soon because the diaphragm is totally developed, it begins to contract at irregular intervals. This motion reduces the intrathoracic stress by enlarging the thoracic cavity and with it the intrapulmonary area. The vocal folds are separated, and thus air rushes into the lungs at atmospheric strain. The small lungs, posterior to a relatively very massive heart, develop in an anterior path on each side of it (Plate 1-38). By the eighth gestational week, the lungs are larger than the center and nearly encompass it. This broad medial septum of viscera and connective tissue is known as the mediastinum. The region where the visceral pleura displays off the lungs and becomes steady with the parietal pleura shifts medially and becomes smaller to envelop the structures that constitute the basis of the lung. The reptilian lung has branching respiratory tubes ending in terminal sacs which might be much like mammalian primitive alveoli. They add greatly to the surface area the place gas trade happens; in distinction, the amphibian lung has solely rudimentary alveoli. The epithelial cells turn out to be so thin when the alveoli fill with air that, earlier than the arrival of electron microscopy, there seemed to be breaks in the lining where only capillary endothelium separated the blood from the alveolar air (see Plate 1-41). The capillaries, covered by the skinny epithelial cells, line the alveolar spaces (see Plate 1-41). These very skinny cells, constituting the major part of the alveolar surface, are often known as sort I pneumocytes. The original mesenchyme that offers rise to the pulmonary capillaries and lymphatics is also the source of the fibrocytes that produce an abundance of elastic fibers in the lungs (see Plate 1-40). After the lungs turn into inflated with air, the elastic fibers are constantly stretched and, by making an attempt to contract, contribute to the conventional recoil or collapsing tendency of the lungs. The resulting adverse pressure in the pleural cavities helps to maintain the lungs expanded.
Discount cytotec 100 mcg overnight delivery
The true diverticulum is mostly congenital in origin and has a mucous membrane lining steady with that of the urethra medicine 2 cytotec 100 mcg cheap with visa, whereas the wall of the false sort is initially an unlined pouch as a result of a neoplastic or inflammatory process medications buy cytotec 200 mcg on-line. Destruction of the mucosal lining of a real diverticulum by inflammation may render the two varieties indistinguishable. A false, acquired diverticulum may become epithelialized following surgical drainage of a periurethral abscess and could also be interpreted as a true selection. Difficult urination (stranguria) or recurrent urinary tract infections are the most typical presenting symptom. In addition, a typical historical past is that in micturition, a mass seems in the perineum, scrotum, or beneath the penis that slowly disappears with dribbling of urine from the urethra. The condition is suspected by statement and palpation of the diverticular mass and the analysis is confirmed by urethroscopy and antegrade or retrograde urethrography. The accent or duplicated urethra could be very rare and has an unknown embryologic origin. They can talk with the true, orthotopic urethra and for the most half are positioned ventral (hypospadiac) to the true urethral channel. The most common kind of urethral duplication is the Y kind, by which a perineal meatus accompanies the usual orthotopic penile meatus. Retention of inflammatory exudates within these accent structures can lead to recurrent abscess formation and intermittent purulent discharge. Infected anomalous tracts could require full marsupialization or excision to eradicate the persistent inflammation. The verumontanum represents the fusion of the terminal m�llerian ducts (see Plate 2-12) and is situated in the posterior urethral floor proximal to the exterior urethral sphincter. The solely identified operate of this construction is to direct the semen throughout ejaculation. Visible modifications embrace easy vascular engorgement or congestion, with or with out edema. Urinary obstruction is rare but attainable, with ballooning of the preputial cavity with urine upon micturition. When infected, the prepuce might turn out to be edematous, enlarged, and pendulous, with purulent discharge oozing from the red and tender preputial orifice. The retention of decomposing smegma, retained urine, and epithelium inside this cavity may lead to ulcerative inflammatory conditions (see Plate 2-21), formation of calculi, and leukoplakia. A phimotic foreskin should be eliminated in any age group as the danger of buying penile cancer is tremendously elevated in uncircumcised males demonstrating poor hygiene and retention of such carcinogenic decomposed secretions. In this condition, venous and lymphatic drainage is impaired resulting in marked edematous swelling of the prepuce and glans penis distal to the constricting ring. As swelling progresses, the influence of the constriction becomes more critical till the retracted preputial pores and skin is unimaginable to manually scale back. Severe infection within the type of cellulitis, phlebitis, erysipelas, or gangrene of the paraphimotic foreskin could happen. In the occasion of failure of Phimosis Adherent foreskin Paraphimosis Strangulation by metallic ring guide reduction, incisions are made within the constricting band of retracted foreskin to relieve constriction (dorsal slit) and allow for swelling to reside before a formal circumcision is carried out. Placing the penis into rigid devices similar to bottles, pipes, and metallic rings could lead to strangulation much like that observed with extreme paraphimosis. Edema, thrombosis, inflammation, gangrene, and sloughing are observed in uncared for circumstances. The situation includes penile curvature or a plaque, penile pain, and erectile dysfunction. A firm, flat, benign nodule or plaque could additionally be felt on the penis and should contribute to curvature. The plaque is located within the tunica albuginea, the robust fibrous covering of the corpora cavernosal bodies. In persistent circumstances, empirical medical therapies include antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and penile stretching devices. Surgical cures are routine with either penile plication (straightening) procedures or plaque excision and grafting procedures and may involve penile prosthesis implantation. Fibrous mass between corpora cavernosa Surgical reparation Early: Thrombosis of corpora cavernosa (engorgement and priapism) Priapism is a chronic and sometimes painful penile erection lasting more than four hours and never associated to sexual need or stimulation. The word is derived from the Roman god Priapus, a deity renowned for his erect penis. Drugs related to priapism include papaverine, phentolamine, prostaglandin (when given for erectile dysfunction), trazodone, propranolol, hydralazine, thioridazine, antidepressants, and cocaine. It can additionally be necessary to find and treat the root reason for ischemic priapism with intravenous fluids, pain medication, oxygen, radiation, or chemotherapy. It happens on account of three mechanisms: external or inner harm or obstructive illness. External blunt or penetrating injuries might contain the penile or bulbous urethra, extra generally the latter because of its immobility. Extensive accidents generally involve the corpus spongiosum surrounding the urethra and Buck fascia, with subcutaneous hematoma formation in the perineum and penis. In cases of urethral tears restricted to the mucosa, the one symptom may be blood on the urethral meatus. With in depth accidents, a Foley catheter could additionally be unable to be handed and there will be the look of a rapidly growing subcutaneous hematoma. Immediate surgical exploration is feasible if the patient is hemodynamically steady, and the severed ends of the urethra could be anastomosed over a urethral catheter. Otherwise, urinary diversion with a suprapubic tube and delayed reconstruction are undertaken both sooner (within 5 days) or later (several months) after the damage with wonderful outcomes. Urination with a urethral injury may find yourself in extravasation of urine into the subcutaneous tissues outside of Buck fascia and beneath Colles fascia, where it spreads alongside identified anatomic pathways (see Plate 2-20). Stricture formation, urinary incontinence, and erectile dysfunction are late sequelae of urethral trauma (see Plate 2-26). Internal urethral accidents result from the passage of sounds, catheters, or international objects by way of the urethra. The penetration normally results in a false passage posterior to the urethra inside the corpus spongiosum. Spontaneous rupture of the urethra proximal to a preexisting urethral stricture could also be due to elevated intraurethral voiding strain. The most devastating complication of this phenomenon is the prevalence of perineal and genital fasciitis (tracking along Colles fascia) because of gram-negative rods or anaerobic micro organism, otherwise known as Fournier gangrene. This life-threatening an infection requires instant and repeated surgical drainage to keep away from overwhelming sepsis and has measurable fatality rates in older, immunocompromised, or diabetic sufferers. Thus, the diploma and extent of urine extravasation depends not solely on the kind and severity of the damage but also on the concerned fascial planes, making data of these fasciae important within the treatment of this condition.
200 mcg cytotec generic overnight delivery
Note: Direct angiographic methods have been supplanted by dynamic computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging medications and grapefruit 100 mcg cytotec with mastercard. Partial hepatectomy includes elimination of a number of segments completed by isolation of the relevant portal pedicle medications with sulfa 100 mcg cytotec discount mastercard, severance of the related hepatic veins, and elimination of the related liver tissue. The nomenclature of those operations is predicated on the anatomic descriptions of Couinaud (1954, 1957) and Bismuth (1982) (Table 2-2). The alternative, extra generally used terminology of Goldsmith and Woodburne (1957) also is listed. A newer terminology has been proposed by the International Hepato-Pancreatico-Biliary Association (Strasberg et al. Laparoscopic techniques, however, can provide useful info relating to the presence of lesions along with those shown on imaging research and in regards to the presence or absence of extrahepatic illness. A, Exploded view to present the sectors (separated by the major hepatic veins) and the segmental structure of the liver, every segment provided by a portal triad. The anatomic division into proper and left lobes by the umbilical fissure and right into a proper and left liver in the principal plane (along the principal scissura) is obvious (see Chapter 1). Ultrasonography is of worth within the preoperative evaluation of a number of tumors and also could help distinguish cysts from strong tumors. Duplex ultrasound permits display of vascular structures, including the hepatic veins and vena cava (Plate 2). Ultrasound is of explicit significance within the preoperative evaluation of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. We have provided some figures of those angiographic techniques for illustrative functions. For the nomenclature of Goldsmith and Woodburne (1957), see Chapter 1 and Table 2-2. The left portal vein accommodates an extension of tumor that protrudes into the primary portal venous trunk. B, Extended left hepatectomy was carried out together with resection of the affected portion of the portal vein and subsequent portal vein reconstruction. The affected person was alive and well without evidence of further recurrence within the liver 10 years postoperatively. A giant, well-circumscribed tumor in the right liver has expanded and is adjoining to the inferior vena cava. Final histology revealed that this lesion was a benign fibrous tumor of the liver. Extended right hepatic lobectomy (right lobectomy) was carried out with out incident. The tumor is compromising and compressing the inferior vena cava and extends upward to involve the proper hepatic vein at its point of junction with the vena cava. Positron emission tomography is now an essential modality in demonstrating the extent of illness. Second, very giant tumors that are pushing structures aside and have been slowly rising over a lengthy time are troublesome to define exactly because strain adjustments can mimic invasion on radiography. The morphologic configuration of tumors as outlined on imaging studies is expounded to resectability. Ultrasound defines the relationship between a colorectal metastasis and the veins on the hepatic vein confluence. A, Transverse ultrasound exhibits the metastasis (asterisk) contacting the inferior vena cava (i) and right hepatic vein (r). B, Oblique intercostal projection confirms that the right hepatic vein is compressed (arrow) but not invaded by tumor (asterisk). Transverse ultrasound shows hilar cholangiocarcinoma on the confluence of the hepatic ducts. The portal vein confluence instantly under the tumor is unaffected, and the portal vein is free. The tumor prolonged into the right hepatic duct, and an extended right hepatic lobectomy was needed due to the tumor extent. A, Selective hepatic arteriogram shows a large pri- C mary hepatocellular carcinoma (arrows). C, Selective splenic artery catheterization and late-phase splenoportogram present extreme compromise of the best department of the portal vein (black arrow). All sufferers with a historical past of cardiorespiratory disease and all sufferers older than age sixty five years undergo a full cardiorespiratory investigation. All sufferers with cirrhosis are assessed rigorously as to the potential for present or past infection with hepatitis B or C, for the presence of alcoholic cirrhosis, and for liver operate according to the Child-Pugh criteria. To obviate air embolism, the dissection is completed with the patient in a 15-degree Trendelenburg position. Control of the central venous strain is maintained at the desired level utilizing a mix of anesthetic methods and intraoperative fluid restriction. A, Endoscopic cholangiogram shows the typical irregular biliary stricture attribute of sclerosing adenocarcinomas (arrow). Position of the Patient the patient is positioned supine with the right arm extended at proper angles to the physique. A cross bar or related gadget must be fitted to the desk, which later holds a self-retaining retractor to elevate the costal margin. Large tumors on the proper side of the liver, especially those lying posteriorly, could require extension as a right thoracoabdominal approach. In specific, the buildings occupying the free edge of the lesser omentum and lymph nodes related to the hepatic artery and the celiac axis and the supraduodenal nodes are assessed. The ligamentum teres is split, and the falciform ligament is incised and separated from the anterior belly wall. A ligature must be left on the ligamentum teres, which acts as a useful retractor throughout subsequent dissection. The lesser omentum must be incised and a finger launched into the lesser sac to permit palpation of the caudate lobe (segment I). To mobilize the right lobe, the peritoneal reflection at the edge of the best triangular ligament is incised and the naked area of the liver on the proper is exposed. If, throughout mobilization of the best liver, the tumor is found connected to the diaphragm, the affected space is separated or a segment of the diaphragm is excised. On the left side, the liver is mobilized by division of the left triangular ligament. Suspicious lymph nodes are taken for frozen section at an early stage of exploration. In cirrhotic sufferers, blood loss could improve during mobilization; this improve is related to a degree of portal hypertension. A, the ligamentum teres is secured, and division of the falciform ligament is begun. A, Incision of the peritoneal reflection of the best triangular ligament permits mobilization of the best liver. Biliary drainage from the remnant should be preserved without biliary leakage and without harm to the biliary tract. When performing extrahepatic dissection for right-sided resections, I normally divide the right hepatic artery and the right portal vein but divide the biliary structures throughout the pedicles at the time of parenchymal transection.
Purchase 200 mcg cytotec with amex
Genetic factors In epidemiological studies medicine buddha mantra quality cytotec 200 mcg, parental history of bronchial asthma is the strongest danger elements in contrast with others symptoms webmd cheap 200 mcg cytotec otc. Protective factors Farm setting Living on a farm, consumption of raw milk, and prenatal and post-natal contact with livestock have been reported to shield in opposition to bronchial asthma and allergy [58]. Vitamin D and asthma On the one hand, there was rising proof for the protecting impact of vitamin D [23, 62]. On the opposite hand, some research have suggested a positive association between the level of vitamin D 44 consumption and risk, for example, of atopic eczema [63]. Vitamin D deficiency might weaken pulmonary defences against respiratory infections and thus set off bronchial asthma exacerbations in infancy and in school age [64]. A possible mechanism of protection is the anti-inflammatory effect of vitamin D lowering the injury caused by viral induced irritation. The effect could also be due to the antioxidants, which may cut back oxidative stress-related inflammatory disease. Secondary prevention Although allergen avoidance was not discovered to be protecting as a major measure [68], secondary prevention can be a successful approach in reducing the decline in lung function and persistent allergic inflammation within the bronchi for sensitised individuals. Children with sensitisation to indoor allergens and who had steady publicity in the course of the first 6 years of life were found to have poorer lung operate than individuals with sensitisation but with out vital exposure. Pharmacotherapy can reduce signs and may achieve bronchial asthma control; however, no influence on the pure course of the illness could be confirmed. However, of those 30% a certain share (approximately 12%, as within the Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study undertaken in New Zealand) relapsed [37]. A optimistic methacholine challenge at 15 years of age predicted a relapse of asthma at 26 years of age in the Dunedin study [74]. There seems to be totally different risk factors for bronchial asthma at the age of 11�13 years in contrast with children starting to wheeze earlier than and after the age of three years. Perennial sensitisation is extra essential in kids with early and later wheeze whereas atopic dermatitis was discovered to be a danger factor for youngsters beginning to wheeze after the age of three years. A child with wheeze before the age of 3 years and sensitisation to indoor allergens (mite, cat or dog) had a chance as high as 75% of still having a wheeze on the age of thirteen years. Impact on quality of life Quality of life (QoL) in chronic asthmatic disease seems to be mainly affected by management; the better the control of bronchial asthma the more enhanced the QoL. Severe uncontrolled bronchial asthma is associated with decreased lung function and impaired performance in physical train and impaired QoL [76]. In Dutch schoolchildren aged 7�10 years, the QoL scores amongst kids and their caregivers have been lower if the child had bronchial asthma with the lowest scores in identified asthma in contrast with undiagnosed asthma and wholesome controls [77]. Lau has acquired an honorarium from Merck for a drug monitoring committee and assist from SymbioPharm and Airsonett for scientific initiatives. Early life danger components for present wheeze, bronchial asthma, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness at 10 years of age. Cultural adaptation is associated with atopy and wheezing among children of Turkish origin living in Germany. Severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy and bronchial asthma and allergy at age thirteen. Respiratory syncytial virus in early infancy: recurrent wheeze and allergy by age 13 years. Maternal smoking will increase the chance of allergic sensitization and wheezing only in youngsters with allergic predisposition: longitudinal analysis from birth to 10 years. Early life elements associated with incidence of physician-diagnosed asthma in preschool children: outcomes from the Canadian Early Childhood Development cohort study. U-shaped association between physique mass index and the prevalence of wheeze and bronchial asthma, but not eczema or rhinoconjunctivitis: the ryukyus youngster health examine. Body mass index in younger kids and allergic disease: gender differences in a longitudinal examine. Incidence and remission of asthma: a retrospective examine on the natural historical past of asthma in Italy. Airway responsiveness in mild to reasonable childhood asthma: intercourse influences on the pure historical past. Influence of gender on rates of hospitalization, hospital course, and hypercapnea in high-risk patients admitted for asthma: a 10-year retrospective study at Yale-New Haven Hospital. Early-life origins of adult disease: national longitudinal population-based study of the United States. Day care attendance, respiratory tract sicknesses, wheezing, bronchial asthma, and complete serum IgE level in early childhood. The sample of sensitization is related to the development of asthma in childhood. Exposure to furry pets and the risk of bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis. Genetic variations in toll-like receptor pathway genes influence bronchial asthma and atopy. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are related to elevated risk of viral coinfections in wheezing kids. Early life environmental management: effect on signs, sensitization, and lung perform at age three years. Reducing domestic exposure to dust mite allergen reduces bronchial hyperreactivity in sensitive children with asthma. New insights into the natural historical past of bronchial asthma: primary prevention on the horizon. A longitudinal, population-based, cohort research of childhood asthma adopted to maturity. Asthma in remission: can relapse in early maturity be predicted at 18 years of age An interplay between filaggrin mutations and early meals sensitization improves the prediction of childhood asthma. The increased ventilation is accompanied by heat and water loss because the inhaled air is warmed up to 37uC and is fully saturated with vapour via its passage down the airways. Consequently, the airways are cooled, giving rise to reflex parasympathetic nerve stimulation with resulting bronchoconstriction. Conservation of heat shall be tried by an preliminary vasoconstriction of the bronchial venules. When stopping exercise, the elevated ventilation ceases, and so the need for conserving warmth gives rise to a rebound vasodilatation. However, the elevated water loss attributable to the saturation of the impressed air because of the increased minute air flow (V9E) in train will increase the osmolality within the extracellular fluid of the bronchial mucosa. The water loss from the bronchial mucosa induces motion of water from inside the cell to the extracellular area [9], thereby causing an intracellular increase within the ion focus [10]. This could result in the discharge of mediators, both newly fashioned eicosanoids and preformed mediators similar to histamine, from intracellular granules and cause bronchoconstriction.

Cytotec 100 mcg with visa
Severe anaphylactic reactions may happen during cyst manipulation or with spillage of cyst fluid symptoms 9 days post ovulation purchase cytotec 100 mcg mastercard. Rupture into the Biliary Tract Intrabiliary rupture is the most common complication of hydatid liver cysts internal medicine order cytotec 100 mcg fast delivery. Minor communications are usually asymptomatic, revealed postoperatively by biliary leakage, whereas major communications trigger obstructive jaundice and cholangitis. The radical technique entails complete excision of the cyst, whereas the conservative technique involves removal of the cyst contents and inactivation of protoscoleces. Surgical Exposure and Protection Before evacuation, mobilization of the liver and of the cyst ought to be minimal to keep away from iatrogenic perforation. The space across the cyst is fastidiously isolated by gauze packs, a first layer soaked with normal saline and a second layer soaked with a protoscolicidal agent. Conservative Surgery Protoscolicidals are injected into the cyst if the aspirated contents are clear, however caution ought to be exercised in the case of closely bile stained or purulent content material for worry of inducing caustic cholangitis. Injection of protoscolicidal agents could also be troublesome because strain inside the cyst can be high. I inject a small amount of saline after which aspirate contents and repeat the injection on a quantity of occasions. Prevention of intraoperative spillage of the hydatid cyst contents is doubtless one of the most important steps of the process. After defending the surgical area with protoscolicidal-soaked gauze, the cyst is entered at its most prominent level. Any cyst projecting past the liver parenchyma, and indeed as a lot cyst wall as possible, is excised. The internal layer of the cyst cavity is gently scraped with a curette so as to detach with any remaining parts of cyst from the residual adventitial layer; any small pouches are also explored. Omentoplasty (omental packing) is the only cavity-management approach that has a preventive effect on postoperative biliary leakage, biliary fistula, and deep-cavity abscess. After unroofing the residual cavity as described, a pedunculated omental flap is common and drawn up into the cavity to obliterate the useless area, and the flap is maintained in place with out pressure with sutures to the pericystic wall. Radical Surgery Radical surgery for hydatid cyst ideally consists of complete removing of the cyst along with the pericyst, including exocysts when present and a few adjoining liver parenchyma. Anatomic and Nonanatomic Liver Resection (Chapters 2 to 5) Anatomic and nonanatomic liver resection is particularly appropriate for peripherally positioned cysts. A formal hepatectomy alongside anatomic lines of the liver, including the hydatid cyst or cysts, is good. The liver resection permits closure of the bile ducts, far from the world of any biliary-cyst fistula. Closed whole pericystectomy is defined by full removal of the cyst by making a surgical airplane just exterior the pericyst layer without opening the cyst. The surgical approach to this airplane is similar to the enucleative techniques described in Chapter 6 however is conducted inside the parenchyma and is more difficult and more more doubtless to be complicated by hemorrhage. The parenchymal transection does allow the suture of vessels and bile ducts throughout the parenchyma. It must be famous that in radical resection or pericystectomy, manipulation of a big cyst may result in rupture. To scale back this risk, some surgeons recommend decompression of the cyst by preliminary needle aspiration or open evacuation and then perform pericystectomy. The vena cava and the right hepatic vein are shown lying behind the unresected membrane. However, conservative surgery with individualized administration of biliary fistula is commonly essential. If hydatid cysts inside the main biliary tree are identified at cholangiography, then widespread duct exploration with removing of cyst materials followed by T-tube drainage is indicated. However, endoscopic papillotomy or sphincterotomy with elimination of cyst contents is another method. Cysts are recognized preoperatively within the common bile duct, or residual cysts are detected postoperatively. In medical follow, albendazole must be administered in a dose of 10 mg/kg physique weight twice every day and may be profitable in up to 74% of sufferers with single cysts treated for three to 6 months. Reduction of viability could be achieved in multivesicular cysts and preoperatively in univesicular cysts when percutaneous or elective surgical procedure is planned. Perioperative prophylaxis is recommended to begin 3 days before the surgical procedure; I favor a course of 6 to eight weeks. The suggestion for postsurgical prophylaxis is 3 to 8 weeks of medication for uncomplicated cases. If there was intraoperative spillage of cyst contents, a course or 3 to 6 months is arbitrarily advised. Intraoperative transcystic cholangiogram reveals fistula within the left biliary system (arrow). Cholecystectomy can additionally be a half of different operations, such as liver resection and pancreaticoduodenectomy. Antibiotic prophylaxis is used, with a single dose given on the time of anesthetic premedication. The cystic artery runs transversely, forming with the cystic duct and bile duct the triangle described by Calot (1891). Dissection of this space should present the anatomic constructions and permit safe dissection. A, the triangle of cholecystectomy restricted by the common hepatic duct, right hepatic duct, cystic duct, and liver. B, the triangle of Calot is limited by the widespread hepatic duct, cystic duct, and cystic artery. Intraoperative cholangiography, apart from displaying unidentified stones or pathology within the intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts, additionally offers a exact view of the anatomy of the biliary ductal system. Technique the fundamental rules of dissecting close to the gallbladder and exhibiting clearly any construction earlier than ligature or part is performed should be respected. The cystic artery is identified and ligated only when its relation with the gallbladder has been proven clearly. Different modes of confluence of the cystic duct and customary hepatic duct (see additionally Chapter 1). Incision and Exposure the incision could also be a small proper subcostal incision or a right transverse incision. Gross gallbladder distention might obscure the cholecystectomy triangle, and puncture of the fundus and aspiration of bile are indicated. Retrograde Cholecystectomy the peritoneum overlaying the hepatoduodenal ligament is incised. It is necessary to hold shut contact with the gallbladder and to show the junction between the gallbladder and the cystic duct. A ligature or a clamp is positioned on the junction of the gallbladder, and a cannula for cholangiography is inserted into the cystic duct. This catheter is fixed by tying the ligature beforehand passed across the cystic duct. Variations in the confluence of the extrahepatic bile ducts and cystic duct (see additionally Chapter 1).
Syndromes
- Chemical peels or topical steroid creams
- Who have HIV
- PET scan to check if the cancer has spread
- Swelling anywhere on the face or in the mouth
- Bladder fistula
- Reduced urine output
Cytotec 100 mcg order online
Most adults with Caroli disease have a unilobar fusiform dilation of the intrahepatic ducts medications in canada purchase 200 mcg cytotec otc, mostly involving the left ductal system treatment neuroleptic malignant syndrome cytotec 200 mcg buy generic. In sufferers with Caroli illness restricted to one lobe of the liver without the presence of concurrent cirrhosis or hepatic fibrosis, hepatic resection, with or with out Roux-en-Y cholangiojejunostomy, stays the remedy of selection. Most patients with diffuse Caroli illness have cirrhosis, persistent recurrent cholangitis, portal hypertension with variceal bleeding, and death secondary to liver failure or carcinoma. Cholangiocarcinoma happens on the biliary confluence, within the mid-duct, or within the distal duct presenting as a periampullary tumor (see also Chapter 10). Three distinct macroscopic subtypes of cholangiocarcinoma are well described: sclerosing, nodular, and papillary (Weinbren and Mutum, 1983). Sclerosing tumors cause an annular thickening of the bile duct, typically with diffuse infiltration and fibrosis of the periductal tissues. Nodular tumors are characterized by a agency, irregular nodule of tumor that tasks into the lumen of the duct. Longitudinal unfold along the duct wall and periductal tissues is an important pathologic function. The papillary variant is delicate and friable and may be associated with minimal transmural invasion. Biliary cancer might arise throughout the intrahepatic biliary tree presenting as a mass or as a biliary cyst. Generally talking, periampullary cancer is handled by pancreaticoduodenectomy (see Chapter 10) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by hepatic resection (see Chapters 2 to 5). Cholangiocarcinoma involving the proximal bile ducts (hilar cholangiocarcinoma) and gallbladder most cancers require biliary resection, with or with no concomitant hepatic resection. Instrumentation and former operation considerably increase the incidence of bactibilia and the chance of postoperative infection and are related to larger morbidity and mortality rates after surgical resection. Segmental or lobar atrophy may outcome from portal venous occlusion or biliary obstruction. One or both of those findings are often present in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. These tumors cause a circumferential thickening of the duct wall and periductal fibrosis, which finally obliterates the lumen. Gross cholangiographic and microscopic appearance of a papillary cholangiocarcinoma (left, A, C, E) and a nodular-sclerosing tumor (right, B, D, F). Note the papillary tumor throughout the bile duct lumen (arrow in A) and the nodular-sclerosing tumor invading the hepatic parenchyma (arrow in B). Transhepatic cholangiogram of a papillary tumor (C) shows a number of filling defects that expand the duct (black arrows; the biliary drainage catheter is indicated by the white arrow). This is in distinction to the cholangiographic options of nodular-sclerosing tumors characterised by an irregular stricture that constricts the duct lumen (arrow in D); a transhepatic catheter is seen traversing the stricture. Histologic section of a papillary cholangiocarcinoma with no invasive element (asterisk in E) and an invasive nodular-sclerosing tumor related to a desmoplastic stroma (F). The left portal vein is occluded, resulting in extreme atrophy of the left liver, which is shrunken and has dilated and crowded intrahepatic ducts. Intraoperative view exhibiting a severely atrophic left lobe of liver, which is clearly demarcated from the proper liver. Abdominal discomfort, anorexia, weight reduction, pruritus, and jaundice are the most common. Segmental obstruction might end in ipsilateral lobar atrophy without overt jaundice. Imaging Cholangiography shows the location of the tumor and the biliary extent of disease. B, Transverse color Doppler ultrasound of the biliary confluence exhibits a papillary cholangiocarcinoma (m) extending into the proper anterior (a) and posterior (p) sectoral ducts and the origin of the left duct (l). The tumor has occluded the right anterior sectoral department of the portal vein, and the anterior sector appears atrophic (indicated by black lines) with crowded, dilated ducts. Similar findings are indicated in this picture, in which the bile ducts seem white. Biopsy specimens of the principle tumor and the intrahepatic metastases confirmed adenocarcinoma. The principal caudate lobe duct, seen joining the left hepatic duct, is also dilated (arrow). Alternative Diagnoses the commonest alternative diagnoses are gallbladder carcinoma, Mirizzi syndrome. Characterization of tumor extent should take into account all obtainable preoperative data associated to local tumor, including the extent of tumor throughout the biliary tree, vascular involvement, lobar atrophy, and metastatic illness. This makes it possible to stage tumors preoperatively in a way that correlates with resectability and end result. A proposed medical staging scheme (Table 9-1) underscores the importance of considering portal vein involvement and liver atrophy in relation to the extent of ductal most cancers unfold. A, Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography shows a attribute large gallstone impacted within the neck of the gallbladder inflicting obstruction of the hepatic duct just under the biliary confluence (arrow). The main limiting issue for resection of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is said to involvement or compression of adjoining vessels and, in particular, one or different department or the principle trunk of the portal vein (Blumgart et al. Laparotomy and Exploration Staging laparoscopy might assist establish some nonresectable patients before committing to a laparotomy (Jarnagin et al. The ligamentum teres is elevated, allowing thorough examination of the subhilar area. Tumor Assessment and Resection the widespread bile duct is first transected above the duodenum and turned upward. The liver hilus is exposed by taking down the gallbladder and reducing the hilar plate. If native bile duct excision is possible, the left and right hepatic ducts are divided above the tumor. The common bile duct is divided immediately above the duodenum, and its lower end has been separated from the underlying portal vein and hepatic artery and elevated together with associated connective tissue and lymph nodes. A director or clamp normally can be passed beneath the liver tissue, above the pedicular structures, allowing secure division of the liver parenchyma. The bridge of liver tissue on the base of the umbilical fissure has been divided (arrows). The biliary confluence and left hepatic duct together with the tumor have been lowered from beneath the quadrate lobe. The whole extrahepatic biliary equipment is elevated together with associated portal connective tissue and nodes to permit dissection anterior to the bifurcation of the portal vein and elevation of the tumor, which is now utterly mobilized. The left hepatic duct has been divided away from the tumor and is held on stay sutures. Its proximal finish, together with the confluence of the bile ducts, common hepatic and customary bile ducts, and the gallbladder, is turned upward and to the proper; keep sutures are placed in the right hepatic duct, which is similarly divided with subsequent elimination of the tumor. After transection of the left hepatic duct and through the retrohilar and retrotumoral dissection towards the proper, one regularly encounters obstructed and dilated ducts issuing from the caudate lobe, and two proper hepatic ductal orifices represent the anterior and posterior right sectoral ducts.
200 mcg cytotec discount overnight delivery
Depending on the location and the arterial supply of the tumor identified before operation medications identification cytotec 100 mcg cheap overnight delivery, the right or left hepatic artery is recognized and traced again to the right hepatic artery symptoms high blood sugar discount cytotec 200 mcg free shipping. Ligation of the right or left hepatic artery for a significant lesion of the best or left liver is usually adequate. Intraoperative photograph exhibits enucleation of a giant hemangioma of the best lobe of the liver. A main department of the center hepatic vein is seen uncovered in the depths of the wound. The lesion can then be compressed and, as tension is relieved, could be clamped (I choose a sponge holder) for traction as dissection proceeds. Division of only some millimeters of liver tissue on the periphery of the hemangioma is often all of the parenchymal dissection required. At this point, a sheath of compressed liver tissue (a pseudocapsule) is encountered that defines the border between tumor and the traditional liver parenchyma. The ensuing hepatic defect after enucleation can be treated in quite so much of methods. Generally, the bleeding from the mattress of the hemangioma is minimal and may be managed by compression and the use of an argon beam coagulator. The method described allows large hemangiomata to be resected with a restricted disruption of the encircling liver tissue. Even when the scale of the tumor means that many of the proper or left liver has been eliminated, the disturbance of liver function is insignificant. Liver metastases are perfused almost solely by the hepatic artery, whereas normal hepatocytes derive their blood supply from the portal vein and the hepatic artery. The use of medication that are largely extracted by the liver during the first pass leads to high native concentrations of drug with minimal systemic toxicity. The development of a completely implantable infusion pump allows for the secure administration of hepatic arterial chemotherapy in the outpatient setting. Excellent definition now may be ascertained utilizing computed tomography angiography. The distal common hepatic artery, the complete gastroduodenal artery, and the proximal correct hepatic artery are dissected. It is essential to mobilize the total length of the extrapancreatic gastroduodenal artery to facilitate insertion of the catheter. Suprapyloric side branches of the gastroduodenal artery are often encountered and should be ligated. The widespread hepatic artery is mobilized 1 cm proximally, and the right hepatic artery is mobilized about 2 cm distally from the origin of the gastroduodenal artery. Branches to the retroperitoneum from the best or left hepatic artery are frequent and should be ligated. Thus, an entire circumferential dissection of the frequent hepatic artery, gastroduodenal artery, and correct hepatic artery should be ensured so that no vessels to the pancreas, stomach, or duodenum are current. The gastroduodenal artery must be briefly occluded with palpation of the right hepatic artery to rule out retrograde flow to the liver through the gastroduodenal artery secondary to celiac stenosis. No attempt at dissection of the common bile duct is important because this dangers devascularization and probably ischemic stricture. A pump pocket must be created within the lower stomach in order that the pump lies beneath the waist and avoids contact with the iliac spine and the sting of the ribs. In obese sufferers, placing the pump over the ribs must be thought-about as a outcome of this will help in finding and accessing the pump. The catheter is trimmed at a bevel just past the last tying ring and is tunneled into the stomach cavity. The gastroduodenal artery is ligated with a nonabsorbable tie at its most distal point, and vascular management of the frequent and correct hepatic arteries is achieved with vascular clamps or vessel loops. An arteriotomy is made in the distal gastroduodenal artery, and the catheter is inserted as much as, but not beyond, the junction with the hepatic artery. The frequent hepatic, proper hepatic, and gastroduodenal arteries are utterly mobilized. With normal anatomy, the catheter is positioned within the gastroduodenal artery and secured with nonabsorbable ties. When positioned, the catheter should be secured two or 3 times with nonabsorbable ties proximal to the tying rings on the catheter. After the perfusion check, the catheter is flushed with heparinized saline, and the injuries are closed. The management of arterial anomalies for pump insertion is a special subject not covered right here but fully discussed by Kemeny et al. In common, one of the best results are obtained if the catheter is positioned within the gastroduodenal artery. When there are replaced or accent vessels to the remnant liver, the surgeon should contemplate the situation of the longer term liver remnant. If the remnant left lobe is fed solely by a changed left hepatic artery, a pump may be placed, but this requires dissection of the left gastric artery and an acceptable side branch for the catheter. Special care should be taken to make certain that all branches to the abdomen have been correctly ligated to forestall extrahepatic perfusion. Occasionally cysts are the major focus of hemorrhage or an infection or produce hepatic dysfunction by bile duct compression or portal hypertension. They are solitary, thinwalled with out focal thickening or nodularity, and anechoic without debris, and they lack septa. Additionally, biliary ductal dilation or intraductal debris may be discovered inside the biliary tree. Cyst hemorrhage and an infection are confirmed by intracystic fluid layering or increased density. Vascular enhancement throughout the cyst wall or mural nodules suggest a cyst-associated malignancy or a cystadenocarcinoma. Finally, cholangiography is essential to differentiate bile duct cysts from hepatic cysts with biliary communication. Simple cysts rarely have true septations however incessantly have intrahepatic portal pedicles, which traverse a portion of the cyst periphery, which may mimic septa. The content material of straightforward cysts is usually serous but may be bile stained, mucoid, bloody, or turbid and thick, the adjacent liver could turn out to be compressed and atrophic, and there may be compression of the adjacent portal pedicles. Symptoms develop insidiously and embrace abdominal fullness or pressure, satiety, and mild dyspnea from cyst growth and compression of adjacent organs. Jaundice might accompany in depth compression of the bile duct confluence or frequent hepatic duct however is very uncommon. The indications for remedy of straightforward cysts are symptoms or associated issues. Simple cysts may be complicated by hemorrhage, infection, rupture into the peritoneal cavity or into the biliary tree or adjoining bowel, jaundice, and very hardly ever portal hypertension. Aspiration ought to never be used as a sole definitive treatment as a outcome of cyst recurrence is for certain. Laparoscopic Cyst Excision Generally, laparoscopic administration must be considered earlier than open laparotomy.

200 mcg cytotec purchase mastercard
Idiopathic epididymal obstruction is a comparatively unusual situation found in otherwise healthy men medicine 2015 100 mcg cytotec purchase fast delivery. Adult polycystic kidney disease is an autosomal dominant dysfunction related to quite a few cysts of the kidney medications without doctors prescription 100 mcg cytotec proven, liver, spleen, pancreas, epididymis, seminal vesicle, and testis. Disease onset normally occurs within the twenties or thirties with symptoms of stomach pain, hypertension, and renal failure. It could be congenital, ensuing from m�llerian duct (utricular) cysts, wolffian duct (diverticular) cysts, or congenital atresia or acquired from seminal vesicle calculi or postsurgical or inflammatory scar tissue. Groin and hernia surgical procedure may find yourself in inguinal vas deferens obstruction, particularly in instances by which the Marlex mesh is used in repair. Bacterial infections similar to tuberculosis, Escherichia coli (in males age >35), or Chlamydia trachomatis might contain the epididymis or vas deferens, with scarring and obstruction that may or will not be amenable to microsurgical restore. If normal, obstruction is confirmed, and formal surgical investigation of the reproductive tract begins with a vasogram followed by microsurgical reconstruction. Surgery additionally makes an attempt to reverse specific pathology and, as such, allows for conception at residence somewhat than in the laboratory. The rise of microsurgery as a surgical self-discipline adopted three advances: (1) refinements in optical magnification, (2) the development of extra exact microsuture and microneedles, and (3) the ability to manufacture smaller and more refined surgical devices. The most commonly performed microsurgical procedure in urology is vasectomy reversal. The most typical reason for vasectomy reversal is remarriage and the need for more children. Occasionally, an unlucky individual will have continual pain after vasectomy or have misplaced a toddler and desire another. Infection, congenital deformities, trauma, and former surgery are less frequent indications for vasovasostomy or epididymovasostomy (see Plate 5-4). Importantly, optical magnification with an operating microscope improves outcomes as smaller sutures can be utilized, decreasing cicatrix formation and failure rates. In the most effective palms, 95% to 99% of sufferers have a return of sperm after vasovasostomy. If the fluid egressing from the vas deferens accommodates no sperm, a second acquired obstruction could exist in the delicate tubules of the epididymis. In this case, the abdominal vas deferens must be connected to the epididymis proximal to the blowout to bypass each websites of obstruction and to reestablish reproductive tract continuity in a procedure termed epididymovasostomy. For epididymovasostomy, the epididymis is uncovered by opening the tunica vaginalis that surrounds the testis. The epididymis is inspected and a person tubule selected that appears dilated and is proximal to the obstruction. With the invagination technique, one, two, or three "vest" microsutures are positioned close to however not into the opening Microsurgical two-layer vasovasostomy Two-layer Modified one-layer Inner layer closure Microsurgical vasovasostomy approaches Outer layer closure Mucosa to mucosa epididymovasostomy Vasal fluid sampling A2 B1 A2 B2 C1 A1 C2 C1 A1 C2 B1 B2 "Vest" suture placement Invagination epididymovasostomy Vasostomy closure after vasogram of the epididymal tubule to enable the epididymal tubule to be drawn into, or "invaginated" into, the lumen of the vas deferens, theoretically creating an improved watertight seal. After epididymovasostomy, roughly 60% to 80% of men could have sperm in the ejaculate. After puncturing or hemitransecting the straight segment of the scrotal vas deferens, diluted dye or contrast medium is injected into the vas deferens toward the bladder from the scrotum. In plain-film radiographs, contrast delineates the proximal vas deferens, seminal vesicle, and ejaculatory ducts and the positioning of obstruction could be decided. With this information, the positioning of obstruction can be accurately decided and the system microsurgically reconstructed with either vasovasostomy or epididymovasostomy. This supplies definitive evidence of either obstructive or nonobstructive azoospermia. The method entails a small, open incision within the scrotal wall and testis tunica albuginea under native anesthesia. Although several wonderful descriptions of testis seminiferous epithelium histology have been reported, no particular person classification has been uniformly adopted as a normal method. With normal sperm production, formal investigation of the reproductive tract for obstruction is warranted, starting with a vasogram (see Plate 5-5). This condition exists in 5% of males with a contralateral germ cell testis tumor and is extra prevalent in infertile than fertile men. A single testis biopsy will detect the presence of sperm in 30% of men with nonobstructive azoospermia. With the multibiopsy method, 4 to six individual testis biopsies are taken from completely different areas of the testis to enhance the odds of discovering sperm in any particular tissue sample. Similar to different "open" or percutaneous testis biopsy strategies, fine-needle aspiration mapping is performed under native anesthesia. It is also a diagnostic procedure that creates a geographical "map" of the testis to justify future and potentially more invasive makes an attempt at sperm retrieval. Percutaneous aspiration sites are marked on the scrotal skin, 5 mm aside, based on a template. The number of aspiration sites varies with testis dimension and ranges from four (to affirm obstruction) to 15 per testis (for nonobstructive azoospermia). After aspiration, the tissue fragments are expelled onto a slide, gently smeared, and stuck in 95% ethyl alcohol. Pressure is applied to every site for hemostasis and a routine Papanicolaou stain is carried out and the slides learn by a cytologist for the presence or absence of mature sperm with tails. Patients with congenital or acquired obstruction of the excurrent ductal system on the stage of the prostate or the pelvic portions of the vas deferens are candidates for vasal sperm aspiration. Also included are males with ejaculatory failure as a end result of diabetes or spinal twine damage. Using optical magnification, a small incision or puncture is made within the delicate wall of the vas deferens until the lumen is entered. Sperm and fluid are aspirated and, after adequate sperm are obtained, the vas deferens wall is closed microsurgically; no closure is needed for a puncture vasotomy. Testicular sperm extraction is indicated for "obstructed" patients and can be helpful for many men with nonobstructive azoospermia. The capability to freeze and thaw retrieved sperm is a significant advance in the care of azoospermic males. After this, ejaculation is the forcible expulsion of semen from the penis in a collection of spurts attributable to rhythmic contractions, about 1 second apart, of the pelvic muscular tissues. Ejaculation is under management of two nervous methods: the sympathetic (autonomic) nervous system governs emission and the somatic nervous system controls ejaculation. Expulsion of the ejaculate is ruled by the somatic nervous system by way of the pudendal nerve (S2-S4). This is a straightforward diagnosis that requires a history of aspermia, with a postejaculate urine sample displaying sperm. Sperm can additionally be "harvested" from the bladder and used for fertility procedures if wanted. Secondary or acquired anejaculation may be as a end result of the same drugs that trigger retrograde ejaculation.
Discount 100 mcg cytotec fast delivery
Noncirrhotic patients in whom clearance of tumor or elimination of benign lesions can be obtained without compromising hepatic arterial and portal venous influx medications rheumatoid arthritis cytotec 200 mcg discount fast delivery, hepatic venous outflow treatment 360 buy generic cytotec 100 mcg line, or biliary drainage to or from the remnant are appropriate for hepatic resection. Postoperative Functional Hepatic Reserve A noncirrhotic, healthy affected person might tolerate a resection of 80% of liver volume. The enormous regenerative capacity permits functional compensation within a few weeks. B, Selective hepatic artery angiogram reveals the gross dimension of the tumor within the left liver. C, Late-phase portogram exhibits gross displacement of the primary trunk of the portal vein and its proper department (arrows). Anteroposterior (D) and lateral (E) views of the inferior vena cava reveal severe compression however no tumor invasion. The tumor proved to be a fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma and was handled by prolonged left hepatectomy. For left-sided resections, dissection within or at the base of the umbilical fissure and nicely to the left of the hilar bifurcation is carried out. Outflow Control (See Chapters three and 4) Intrahepatic management of the hepatic veins carried out during parenchymal transection can be practiced for tumors that allow clearance superiorly with enough tumor margins and with safe access. Extrahepatic dissection and management of the most important hepatic veins is possible in nearly all cases, even for difficult tumors that lie excessive and posteriorly, and it also allows good clearance along with reliable management of hemorrhage. An anterior method can also be used with advantage in such cases, with the vena cava and hepatic veins approached by the preliminary splitting of the parenchyma with out mobilization of the liver (Lai et al. Inflow Control and Preservation of the Integrity of the Biliary Tree (see Chapters 3 and 4) Control of the hepatic arterial and portal venous blood provide to the portion of liver to be eliminated can be obtained by extrahepatic dissection or, alternatively, by transecting the relevant pedicles throughout the liver substance. B, Initial parenchymal dissection (1) with intrahepatic management of the vessels (2). C, Initial dissection of the portal triad and clamp (1) followed by parenchymal transection (2) with intrahepatic control of the vessels (3). D, Intrahepatic management of the portal pedicles (1) followed by parenchymal transection (2) with subsequent intrahepatic management of the hepatic veins (3). A Kelly clamp is used to crush the liver tissue and expose vessels for clipping or suture ligation. During this part of the operation, we apply intermittent inflow occlusion (Pringle, 1908) to management blood move to the remnant, often sustaining inflow occlusion for intervals of 5 minutes interspersed by 1-minute durations of aid to allow perfusion of the remnant and decompression of the bowel. Several different methods have been developed, together with bipolar cautery, a saline-linked radiofrequency ablation gadget, and the harmonic scalpel. Although I have not used these techniques, they could be notably useful within the performance of laparoscopic partial hepatectomy. In latest years, stapling strategies have been used to divide main vessels and pedicles inside the liver substance and for parenchymal transection (see Chapter 3). The establishment of drainage is related to a prolonged hospital keep, an elevated possibility of an infection, and no lower within the want for postoperative interventional radiology� directed drainage. Drainage of the best subdiaphragmatic area with easy large-bore drains connected to a closed system or to a suction apparatus. The cystic duct is transfixed earlier than being ligated, and a tie is left on the cystic duct for later retraction. It is best to dissect the best hepatic artery and portal vein and to depart management of the right hepatic duct until later in the operation. The main portal trunk is exposed, and the left department is recognized and preserved. Sometimes the best anterior and posterior sectoral branches of the portal vein arise individually (see Chapter 1), and these origins could additionally be separated by as much as 2 cm. Care should be taken not to injury the first posterior caudate department of the right portal vein. Application of a straight-bladed vascular clamp is a protected technique of transecting the right portal vein. The hepatic bile duct or its main sectoral tributaries are normally secured in the pedicles (see the following) additional laterally at the time of parenchymal dissection. However, deliberate dissection of the hepatic ducts should be carried out for tumors that approach the hilus of the liver. The confluence of the bile ducts and the infrahepatic course of the left hepatic duct should be identified after lowering of the hilar plate. The hilar plate is lowered to expose the left hepatic duct and the confluence of the bile ducts. This maneuver opens the umbilical fissure and allows better exposure of the subhepatic and hilar space. When the best hepatic duct is dissected, it should be transfixed, ligated, and divided. In many situations, the ducts draining the anterior and posterior right sectors are discovered coming into the confluence individually, or the posterior sectoral duct could join the left hepatic duct (see Chapter 1). In such cases, both these major sectoral ducts ought to be individually identified and secured. This technique allows the surgeon to dissect and clamp the required sheaths early within the operation and define the segment or segments to be eliminated. It is necessary to ligate and divide the lowermost retrohepatic veins draining from the caudate course of and decrease part of the liver to the vena cava. Failure to do that may lead to hemorrhage throughout passage of a finger or dissector. Care should be taken to respect the anatomy of the pedicles, in particular the pedicle to the best posterior sector. A, the right hepatic duct is dissected (we now, more usually than not, depart the proper hepatic duct for intrahepatic management during parenchymal transection; see text). B, the right hepatic duct has been transfixed with absorbable suture material, divided, and ligated or oversewn. Traction on the sutures attached to the cystic duct and the best hepatic duct stump permits retraction of the frequent hepatic duct and customary bile duct to the left and assists in displaying the vessels beneath. The proper hepatic artery is dissected, ligated, and divided, normally to the proper (as shown) but typically to the left of the frequent hepatic duct. Special care is taken not to harm the primary (caudate branch) of the right portal vein. The left portal vein and the anterior right sectoral vein come up on the identical point. It is essential to acknowledge this variant anatomy and to establish all branches throughout dissection. The liver has been mobilized from the inferior vena cava by division of the retrohepatic veins lying behind the caudate course of. Hepatotomies have been made in the area of the gallbladder fossa and the caudate process. The curved double-headed arrows indicate the sites of the hepatotomies above and beneath the porta hepatis.

Cytotec 200 mcg low price
The innominate artery sometimes traverses the trachea at the degree of the ninth tracheal ring symptoms your having a boy cytotec 100 mcg cheap online, though it might also accomplish that between the sixth and thirteenth rings medicine x pop up cytotec 200 mcg effective. Patients often current with peristomal bleeding or hemoptysis, which could be mild, moderate, or severe. An instant complication is laryngospasm, which may require reintubation or tracheostomy. If the tracheostomy tube turns into dislodged, reinsertion is typically tough, particularly with a fresh tracheostomy. However, chest physiotherapy, together with postural drainage, percussion, aided coughing, and vibratory constructive expiratory stress units, can be fairly efficient and are more acceptable to alert and oriented sufferers. The major indication for nasotracheal suction is the semicooperative or obtunded affected person who requires tracheobronchial bathroom. A 14-Fr suction catheter, held with a sterile-gloved hand, is then passed via the nasopharyngeal airway and superior with each inspiratory part of respiration. Whereas roughly 90% of attempts to attain the tracheobronchial tree by this methodology are profitable, the success fee for blind nasal passage ranges from 10% to 70% relying on the operator. The catheter is then withdrawn while the operator intermittently makes and breaks suction (set between one hundred and 160 mm Hg) over a period of 15 to 25 seconds. Nasotracheal suction of left-sided secretions usually is commonly ineffective, and bronchoscopic removal have to be used. Patients requiring mechanical air flow usually require "inline" suctioning because the presence of the endotracheal tube keeps the glottis patent, limiting the technology of sufficient intrathoracic pressure to adequately clear secretions. Suctioning via a tracheostomy tube is carried out in an identical fashion, utilizing the inline methodology if the patient requires mechanical air flow and the "sterile" method if the patient is receiving supplemental oxygen through a humidified "trach collar. Erosions caused by suctioning permit colonization and penetration of the mucosa by pathogens as properly as cessation of the host mechanism of mucociliary transport. Avoiding continuous suctioning and the use of a weaker vacuum are probably to minimize the damage, however unfortunately, effectivity of secretion aspiration can be diminished. The blue line reveals ramped airway strain (Paw) applied throughout inspiration in response to a square-wave flow pattern shown in purple. Flow and volume are then the dependent variables determined by respiratory system compliance and resistance, and this mode of ventilation is called pressure-control air flow. The inflation stress is ready by the operator, the ensuing volume delivered is the dependent variable. A Stewart or Connell stitch is taken in every margin of intact posterior wall with care to not injure recurent laryngeal nerves Respiratory System C. End-to-end anastomosis completed with fine wire, monofilament, or absorbable suture B. If only two or three rings require excision, approximation and suture could additionally be achieved with assist of head flexion Tracheal stenosis can be idiopathic but is mostly the results of prior intubation or tracheostomy. Mid- to distal tracheal resections are extra doubtless carried out as therapy for benign or malignant airway tumors. In most instances of symptom-producing stenosis of the trachea, conservative therapy, consisting of repeated dilatations, is either contraindicated or has confirmed to be ineffective. In the former occasion, the strategy is by way of a transverse cervical incision; in the latter case, a full or partial (upper) median sternotomy or a fourth intercostal space proper posterolateral thoracotomy may be required. Low intrathoracic tracheal lesions are more easily approached by way of a posterolateral thoracotomy, although some surgeons choose a transpericardial approach accessing the trachea and primary carina between the ascending aorta and superior vena cava through a sternotomy. Preoperative examine of the situation and extent of the lesion utilizing each fiberoptic bronchoscopy and computed tomography is crucial; the situation have to be additional evaluated on the time of surgery. Usually, the stenotic phase may be recognized by the "hourglass" constriction of the outer tracheal wall. Only the diseased area of the trachea should be dissected circumferentially to protect the segmental Mylohyoid muscle (geniohyoid underneath) Hyoglossus muscle Stylohyoid muscle Posterior belly of digastric muscle Middle constrictor Superior laryngeal nerve and artery Inferior constrictor Esophagus G. To relieve pressure on the reconstruction, both inferior pulmonary ligaments are divided, and a pericardial release is performed by opening the fibrous pericardium in a "U" fashion round the best inferior pulmonary vein and dividing the frenulum of sentimental tissue attachments of the pericardium to the atrium blood provide of the remaining airway. For benign illnesses, dissection ought to be instantly on the airway cartilage to forestall injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerves that cross close by within the tracheoesophageal groove. As the anastomosis is being accomplished, the surgeon assesses the reconstruction for tension. A host of pathologic entities is concerned, and for many of these, surgical excision is the remedy of selection. Recognition and identification of mediastinal abnormalities are nearly all the time primarily based on chest radiographs. Vascular tumors (aneurysms, anomalies, angiomas) might happen wherever within the mediastinum. The chance of malignancy relies on the placement, the age of the affected person, and the presence of symptoms. Two-thirds of mediastinal tumors are benign, however those within the anterior compartment are more probably to be malignant. The peak incidence of main malignancy situated within the mediastinum is between the second and fourth many years of life. Most center visceral and posterior compartment mediastinal tumors could be approached surgically by the usual posterolateral incision with the hemithorax entered at an appropriate stage on the aspect of maximal projection of the lesion. Most such tumors are readily shelled out, and their blood provide is easily identified. Although an anterior mediastinal lesion may be handled by the lateral method, most surgeons favor a median sternotomy, as proven. This is the popular incision for thymic tumors, notably within the presence of myasthenia gravis by which full extirpation of all components of thymic origin is desired. A partial sternal splitting incision extended into an anterior thoracotomy (hemi-clamshell) or bilateral transverse sternothoracotomy (full clamshell) incision, however, is now fairly commonly used (for bilateral lung transplantation), is reasonably speedy, and affords entry to both pleural cavities. Resection of only a quantity of segments has the advantage of eradicating solely diseased buildings and leaving wholesome, functioning lung tissue that ordinarily could be eliminated if the excision involved the whole lobe. When the resection is for cancer, the oncologic precept of inclusion of regional draining lymphatics and nodes is preserved. Depending on individual circumstances, the segmental bronchus is recognized and approached first by palpation or the segmental artery first by dissection. The major pulmonary artery, or the continuing pulmonary artery, is identified in its proper anatomic location, and the perivascular sheath is entered. After division and closure by stapling or by suture, a clamp is left on the distal portion of the severed bronchus, subsequently to be used for traction. However, the veins are regularly recognized solely as branches in the intersegmental airplane. Wedge resection has been made easier by the supply of stapling-cutting devices that lay down two or three rows of staples on both aspect and divide lung tissue in between these rows. Not solely should the important lobar buildings be individually recognized and managed by the surgeon, but the remaining structures should be painstakingly protected and preserved. Incomplete fissures may add to the issue, and the surgeon should possess a exact knowledge of hilar anatomy and common anomalies.
