
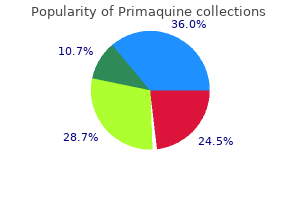
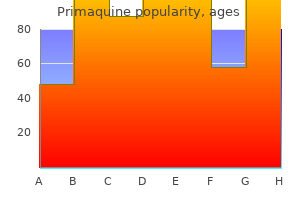
Primaquine dosages: 15 mg
Primaquine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 240 pills, 300 pills

Trusted primaquine 15 mg
It has been instructed that Burkitt lymphoma is a malignancy of post-germinal middle B cells symptoms in dogs primaquine 15 mg generic free shipping, as a outcome of the tumor cells carry a comparatively excessive load of mutations within the Ig variable-region genes (Chapman et al treatment 2 degree burns 15 mg primaquine cheap mastercard. However, cell strains derived from sufferers with Burkitt lymphoma that spontaneously mutate their Ig genes in vitro have been described (Sale and Neuberger, 1998), which suggests that the association between acquisition of mutations within the Igvariable regions and the germinal microenvironment may not be absolute in Burkitt lymphoma. The prognosis of Burkitt lymphoma is largely influenced by the stage of disease on the time of prognosis. In endemic Burkitt, localized disease has a superb prognosis, with speedy regression after remedy and a potential for long-term remission. Nonendemic Burkitt may show an identical preliminary speedy response but the prognosis is ultimately poor, with relapse inside a few months. In a minority of cases, resection of a localized tumor could be adopted by lengthy remissions. Dissemination happens and should contain distant extranodal sites, together with the mind and large gut. In a minority of those instances the distant site will be the website of preliminary presentation. Elsewhere both the endemic (African) form and the nonendemic sort of Burkitt lymphoma commonly contain the gastrointestinal tract (Lennert and Feller, 1990). The disease is extra common in boys and reveals a peak incidence between four and 5 years of age. There is a predilection for the terminal ileum however any a half of the gastrointestinal tract may be concerned. Macroscopically, the lesions may form a localized obstructing tumor mass or could contain large segments of the intestine. Histologically, the mucosa is effaced by cohesive sheets of monomorphic blasts of uniform measurement with spherical nuclei and two or three central nucleoli. Interspersed between the neoplastic cells are phagocytic histiocytes, giving a characteristic starry-sky look. The variety of Ki-67+-proliferating cells is high, with a median of 80% optimistic cells. It has been advised that a very gluten-free food regimen for celiac sufferers could additionally be protecting against the event of lymphoma and that risk is expounded to gluten publicity (Holmes et al. The tumor is usually multifocal, forming ulcerating nodules or large plenty that may be related. In most circumstances, the lymphoma has disseminated at the time of diagnosis, mostly to the liver, spleen, bone marrow, lung, or skin. The most attribute histological look is that of a highly pleomorphic tumor with quite a few multinucleate forms. There is commonly intensive necrosis and a heavy inflammatory infiltrate, incessantly containing many eosinophils. In most circumstances the small gut remote from the tumor reveals histological modifications equivalent to these of celiac illness. The degree of intraepithelial lymphocytosis could also be extreme and should spill into the lamina propria. In these circumstances the lymphocytes are small and lack neoplastic options, but have been shown to be part of the neoplastic clone in a minimal of two circumstances. Mesenteric lymph node involvement may be predominantly intra-sinusoidal, paracortical, or each. The pleomorphic tumor cells can be seen in higher-power; (b) and (c) illustrate the irregular mucosa away from the tumor mass. The tumor tends to be transmural and could additionally be associated with villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, and infiltration of the tumor into the epithelium. Most categorical the form of the T cell receptor, although around 10% categorical T cell receptor and a few are T cell receptor silent. Regression of main gastric lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue type after treatment of H. Primary follicular lymphoma of the small gut: alpha4beta7 expression and immunoglobulin configuration recommend an origin from local antigen-experienced B cells. Treatment of alpha chain illness: results of a prospective research in 21 Tunisian patients by the Tunisian-French intestinal lymphoma research group. The infiltrate is composed of small lymphoid cells that fill the lamina propria with a minor infiltration of the epithelium. In one affected person a novel translocation, t(4;16)(q26;p13) that concerned the interleukin-2 gene was demonstrated. The scientific course was slowly progressive with extended survival but a poor response to therapy (Srvcek et al. The tumor is commonly featured by diffuse irregular ulcers, adopted by tumor masses, that are frequently accompanied by stricture. The tumor cells are medium to large pleomorphic lymphoid cells with angulated nuclei and moderate cytoplasm. Extensive small intestinal T-cell lymphoma of low-grade malignancy related to a new chromosomal translocation. Leukemic manifestation in a case of alpha-chain illness with multiple polypoid intestinal lymphocytic lymphoma. Regression of immunoproliferative small intestinal disease after eradication of H. Enteropathy-type intestinal T-cell lymphoma: scientific features and therapy of 31 sufferers in a single middle. The response of cells from low-grade B-cell gastric lymphomas of mucosa related lymphoid tissue to H. Primary B cell lymphoma of salivary gland and its relationship to myoepithelial sialadenitis. Expression of costimulatory molecules in low-grade mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphomas in vivo. Diffuse lymphoma of the intestines with a monoclonal gammopathy of IgG3 kappa kind. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is effective within the therapy of early-stage H. Immunoproliferative small intestinal illness associated with Campylobacter jejuni. Prognostic worth of translocation t(11;18) in tumoral response of low-grade gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue sort to oral chemotherapy. Nonsecretory alpha-chain disease with immunoproliferative small-intestinal illness. Lack of association with translocation t(11;18): a 10-year up to date follow-up of a prospective examine. Translocations involving the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus predict higher survival in gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nonsecretory variant of immunoproliferative small intestinal illness: a case report with pathologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular findings.

Purchase primaquine 7.5 mg mastercard
These polysaccharides and proteins and the sequences derived from them hold promise as antigens for anti-P medicine 524 cheap 7.5 mg primaquine fast delivery. There are experimental circumstances Table 5) during which immunization can intrude with periodontal bone resorption medications metabolized by cyp2d6 discount 7.5mg primaquine with visa. However, generally Table 5) the experimental periodontal bone loss was related to infection with a single bacterial species. Alveolar bone loss was induced by infection with multiple periodontal pathogenic bacteria. Immunization Studies in Nonhuman Primates Nonhuman primates provide benefits to the development of periodontal vaccines. The anatomic construction of the periodontium, periodontal microflora, host immune responses, and protection mechanisms intently resemble these of humans. Many monkey species develop spontaneously occurring periodontitis as they age but this illness takes a few years to develop and varies significantly. This problem has been circumvented by placement of ligatures at the gingival sulcus that act as enhancers of biofilm accumulation. Ligatureinduced lesions manifest an inflammatory response very related to that seen in human periodontitis that results in alveolar bone destruction. Several immunization research have been carried out with nonhuman primates Table 6). Immunized animals developed high serum IgG to antigens of the immunizing microorganism. Over a interval of one hundred days, the share of immunized animals contaminated within the ligated quadrant remained significantly decrease than within the shamimmunized group. Thus, immunization is related to a discount within the emergence of indigenous P. Groups of monkeys had been immunized with each of the vaccines and a fourth group received placebo vaccine (adjuvant, no bacteria). Three adjacent enamel in a single quadrant had been ligated, and the contralateral enamel have been nonligated controls. Significant increases in serum IgG, IgM, and IgA antibody of all three isotypes had been noticed within the immunized animals and resulted in a significant decrease in P. After immunization, ligatures have been placed across the second premolar and first and second molars in one mandibular quadrant and the contralateral maxillary quadrant was nonligated. Control animals manifested twice the amount of alveolar bone loss as the immunized animals. At week 30 subgingival plaque, blood, radiographic, and clinical measurements have been taken. Alveolar bone loss was greater in the controls than in Mucosal Vaccines for Dental Diseases Chapter 69 1377 immunized animals (see Table 6). With use of the model above and a protocol virtually similar to that of Persson et al. Five young grownup monkeys were immunized over sixteen weeks, and 5 controls acquired adjuvant solely. The Mucosal Immune System in Periodontal Infections Whereas initial research advised that salivary antibodies have potential for diagnostic or protecting features of periodontal disease assessment (Taubman et al. Saliva has been studied as a supply of immunological and different parts that relate to periodontal illness (Ebersole et al. The effects of salivary IgA on periodontal illness manifestations in people may be extremely complex. Salivary antibody to periodontal pathogens may be detected after an infection (Smith et al. Perhaps essentially the most compelling evidence for the association of microorganisms with illness is the sturdy relationship between the prevalence of organisms and gingival and salivary immune responses (Ebersole et al. Both protective and destructive gingival irritation and immunity seem to be inextricably related within the host response to periodontal an infection. These include the power to mixture micro organism, inhibit adherence colonization, and detoxify endotoxins and exotoxins. Examination of these capabilities in periodontal illness has typically tried to relate the levels or presence of antibody activity to the severity of illness and study the power of antibodies to inhibit colonization and to inhibit or antagonize different proposed virulence components of the bacteria (Ebersole and Taubman, 1994). One can suggest that in developing a vaccine an try ought to be made to maximize the potential for mucosal immunity, as a end result of this might be intrinsically the safest technique of immunization. Challenges are concerned in the development of a safe and effective periodontal vaccine. The presence of periodontopathic bacteria in the subgingival flora is important but inadequate for periodontitis to happen. Of equal importance, several bacterial species appear to be concerned (Haffajee and Socransky, 1994; Socransky et al. Alternatively, species related to disease may categorical shared antigenic epitopes. Even if several species are important to the initiation of periodontitis (polymicrobial), a successful vaccine should be possible. Characterization of the epitopes of pathogenic operate of significant antigens of each species liable for induction of protecting immunity may end in dedication of the peptide sequences containing the necessary epitopes. These antibodies mediate their effects by inhibiting preliminary colonization, hence limiting infection by periodontal pathogens of the oral cavity and adjoining tissues. Some of this effectiveness can most likely be attributed to the effective generation of secretory IgA antibody most likely in saliva. This has been described for native immunization and for intranasal immunization and has also been demonstrated for different novel mucosal vaccine induction strategies. Also, there are results of various bacterial parts as antigen and in addition novel adjuvants Table 7). Therefore, the mixture of mucosal antibody and serum antibodies and gingival crevice fluid antibodies can intervene with the era of periodontal bone destruction involving periodontal pathogens generally. This combined mucosal and humoral immunity might exceed humoral immunity alone in protective capabilities. However, periodontal illness in people might contain a extra polymicrobial an infection. Such an infection could require extra refined immunization strategies to generate the immunity required to intrude with a monobacterial an infection. This mode of immunization induced both serum IgG and salivary IgA anti-fimbrial antibody, which appeared to lead to a discount in bone loss related to P. This resulted in significant fimbrial-specific secretory IgA antibody in saliva and serum IgG antibody and reductions in P. Immunized mice confirmed elevated secretory IgA antibody to fimbriae and protection from P. Humoral Immunity of Mucosal Tissues Antibodies derived from serum are discovered in the gingival tissue and could additionally be efficient at enhancing phagocytosis by neutrophils within the gingiva, gingival crevice, or periodontal pocket. In addition, humoral antibodies might exert their protecting effects by neutralizing toxin-like actions of periodontopathic micro organism. Toxins such because the leukotoxin of Actinobacilli have been proven to be neutralized by antibody, and Aggregatobacter are opsonized and phagocytosed by neutrophils. Other mechanisms by which antibodies may exert protective results, corresponding to neutralizing bacterial-derived host cell lytic enzymes.
Syndromes
- Depression and anxiety
- Bilirubin levels are high in blood and urine
- Smoking and smokeless tobacco
- Dry cleaning fluids
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Other lung disease
- Begin teaching your child to drink from a cup at around 6 months of age. Try to stop using a bottle by age 12 - 14 months.
Order primaquine 7.5mg on line
The alternative pathway is pushed by Th2 cytokines within the local milieu leading to medicine 2015 generic 7.5mg primaquine M2 macrophages; this process is necessary within the protection against helminths medicine 8162 15mg primaquine buy otc, humoral immunity, and tissue restore (Martinez et al. Remarkably, the M2 phenotype poor in phagocytosis and killing of germs similar to S. Cytokines produced by M1 macrophages stimulate cytotoxic T cell response and amplify innate antipathogen immune response. M2 macrophages amplify allergic T helper 2 (Th2) response by producing cytokines and chemokines and by recruiting eosinophils, basophils, M2 macrophages, and Th2 cells. Nasal Immunity, Rhinitis, and Rhinosinusitis Chapter a hundred 1903 cytokine profile and asthma comorbidity. An grownup will expertise two to five colds per year, with larger an infection charges in girls aged 20�34 years, in all probability as a result of the exposure to their kids. Children experience six to eight colds per 12 months with a lower rate of respiratory sickness in the first six months of life as a end result of maternal antibodies. The an infection can spread to the center ear by way of the Eustachian tube and to the decrease airways, leading to cough and irritation of the bronchi. Symptoms are self-limiting within 10�14 days, if not followed by an acute postviral rhinosinusitis (Rosenfeld et al. The viral load is strongly correlated with the severity of both decrease respiratory symptoms and increase in bronchial hyperreactivity. A research in internal metropolis asthmatic youngsters additionally confirmed that therapy with anti-immunoglobulin (Ig) E improved asthma management, lowered the necessity for bronchial asthma treatment, and almost eliminated seasonal peaks in exacerbations induced by viral infections (Busse et al. This would point out that apart from the deficiency in Th1 responses, the Th2 response can be contributing to the mucosal defect in these patients. Postviral rhinosinusitis is reflecting the reality that viral infection leads to an inflammatory reaction of the nasal and paranasal mucosa, which persists for a number of days after the viral replication. Secondary bacterial an infection is assumed to complicate solely a very small share of cases (0. Fulminant courses of illness might lead to orbital or cerebral complications within hours or days, either as a result of the virulence of the bacteria or the immune standing of the patient. Vitamin C prophylaxis might modestly cut back the length and severity of the chilly within the common inhabitants and will reduce the incidence of the sickness in a selected group uncovered to physical and environmental stresses. Air air pollution, exposures to cigarette smoke, and allergic irritation has also been shown to impair ciliary function, predisposing patients for colds (Monto and Sullivan, 1993). In allergic rhinitis, as in other allergic illnesses, the immune response begins with sensitization. Following allergen exposure of the upper airway mucosa, allergens are captured and processed by antigen-presenting cells and introduced to na�ve T cells. The presence of these cytokines together with the ligation of appropriate co-stimulatory molecules, promotes B cell class switching to IgE manufacturing. The allergic response can be divided into two phases: the immediate or early-phase response and the late-phase response (Hansen et al. Mast cells and basophils are the best-known IgE effector cells and are responsible for the acute section of airway inflammation. These mediators collectively cause blood vessels to broaden and leak and produce mucosal edema plus watery rhinorrhea. Glands secrete mucoglycoconjugates and antimicrobial compounds and dilate blood vessels to trigger sinusoidal filling and thus occlusion and congestion of nasal air passages. Released mediators additionally stimulate sensory nerves, which evoke the sensations of nasal itch and congestion, and recruit systemic reflexes similar to sneezing. The above responses develop within minutes of allergen publicity (Skoner, 2001; Hansen et al. The response is characterised by infiltration of the mucosa with inflammatory cells, similar to monocytes, T cells, eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils (Abbas, 2014; Hansen et al. It impacts up to one-third of the grownup inhabitants and causes illness and incapacity worldwide (Bachert et al. Causative allergens are primarily inhaled aeroallergens, corresponding to pollens, molds, mud mites, insects, and animal dander. Indoor and out of doors air pollution, as well as socioeconomic differences, are probably necessary elements, however more knowledge are required on these matters. The so-called hygiene speculation postulates that infections and unhygienic contact might confer protection towards the development of allergy (Strachan, 1989; Bousquet et al. The tendency to develop an allergic immune response is inherited by atopic patients (Skoner, 2001). Allergic illnesses, corresponding to rhinitis and bronchial asthma, show sturdy familial and intraindividual clustering and have intently related phenotypes, suggesting an overlapping illness etiology (Bousquet et al. These cells contribute to the clearance of allergen-IgE complexes and phagocytose and kill pathogens. Both the early-phase and late-phase responses in allergic rhinitis can be characterized by signs of sneezing, rhinorrhea, and nasal congestion. It is clear that IgE is a key player in the induction and maintenance of allergic inflammation (Dullaers et al. Hence, the sites of IgE manufacturing in human topics and the nature and characteristics of IgE-producing cells are of nice curiosity. Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis the treatment of allergic rhinitis combines allergen avoidance, pharmacotherapy, immunotherapy, and schooling (Bousquet et al. Key players in the pharmacotherapeutic strategy are H1-antihistamines (oral or intranasal) and intranasal corticosteroids, which also may be mixed for topical remedy. Other pharmocotherapeutic choices include montelukast, topical cromones, and ipratropium, although less effective (Bousquet et al. The mode of action of intranasal corticoids is expounded to their anti-inflammatory activities. Other results of corticosteroids are reduction of the variety of neutrophils and tissue macrophages, blockage of the manufacturing of arachidonic acid metabolites, and reduction of blood circulate and vascular permeability (Meltzer, 2011). These mediators cause the acute indicators and symptoms related to early-phase reactions: � Increased vascular permeability, plasma extravasation, increased mucus secretion and blood vessel dilation, leading to watery rhinorrhea, mucosal edema and congestion of nasal air passages. Also T cells that recognize allergen-derived peptides launch merchandise that contribute to late-phase reactions. These mediators cause the acute signs and symptoms associated with early-phase reactions. Increased vascular permeability, plasma extravasation, elevated mucus secretion and blood vessel dilation result in watery rhinorrhea, mucosal edema and congestion of nasal air passages. Stimulation of sensory nerves of the nostril leads to sneezing and sensations of nasal itch and congestion. Some of the launched merchandise can have anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive features.
Primaquine 7.5mg order with visa
A neutralizing epitope of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus symptoms lymphoma purchase 7.5 mg primaquine with amex, the capsid precursor polypeptide of foot-and mouth-disease virus treatment quadricep strain buy 7.5mg primaquine fast delivery, and the glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus have been expressed in the rice seeds and showed oral immunogenicity for the induction of virus antigen-specific immune responses (Huy et al. For the purpose of continuous delivery of allergen via an oral route for the induction of oral tolerance, the transgenic rice system has been adopted for the technology of rice seeds expressing allergenic proteins (Takagi et al. To reduce undesired anaphylactic reactions that could be elicited through the oral desensitization course of using allergens, the transgenic rice crops expressing T-cell epitope peptides from pollen allergens of Japanese cedar. These information supported a chance for the difference of transgenic rice seeds expressing allergen-specific T-cell epitopes for oral supply and induction of oral tolerance in opposition to pollen allergenspecific responses. In addition to this direct hyperlink between animal and human health, veterinary illnesses indirectly affect public well being and well-being through their probably devastating impact on food manufacturing and trade. There is a rising need for the event of safe, efficient, and reasonably priced veterinary vaccines. Plant-based production platforms may help to meet a few of the specific requirements for the development of profitable and economically viable animal vaccines: the cost of manufacturing within the case of veterinary vaccines must be very low so as to allow the vaccine to find broad use in the farming community, particularly in creating nations where these vaccines are often most wanted (Rybicki et al. Veterinary vaccines will ideally be steady and not require chilly chain storage and transport; expression of vaccine antigens in plant storage organs corresponding to seeds and tubers supplies a protective storage car. Most importantly, any vaccine must be safe and effective at protecting the immunized animal from the target disease: Plant-production techniques have been used to express protecting vaccine candidates, with out the chance of contamination with animal pathogens. Since the transmission routes of many animal pathogens are fecal-oral, respiratory, or through direct contact resulting in infection via mucosal surfaces, vaccines concentrating on these ailments should elicit a robust mucosal immune response in order to be efficacious. Plants significantly lend themselves to the development of oral vaccine candidates for stimulating mucosal immunity. Foot-and-mouth illness is to this present day one of the most devastating ailments affecting farmed animals and wild ruminants worldwide, causing economic losses associated with a high morbidity rate and containment procedures involving culling and motion restrictions. Current vaccines are based mostly on inactivated virus, with safety risks associated with its production. Serum IgG and mucosal IgA were detected after the first 2 weeks of a 4-week feeding regimen of five weekly doses of 10 g P1 antigen. Immunogenicity of the particles was shown by parenteral administration in rabbits. Both viruses are members of the Morbillivirus genus of the Paramyxoviridae and might cause severe ailments in cattle and small ruminants, respectively. Later immunogenicity checks in mice revealed that oral vaccination induced serum IgG and IgA (Khandelwal et al. These results demonstrate that plant-produced edible vaccines can elicit sturdy immune responses in giant animals. The illness is principally related to fertility problems in infected cattle and might lead to abortion and malformations of calves. In a quest to develop a safer various to the commercially out there inactivated vaccine, current progress has been made by two groups in Argentina utilizing plant expression systems. It will be attention-grabbing to see whether or not these vaccine candidates can stimulate mucosal responses in cattle when applied on to the mucosa. Calves are prone to the illness inside the first 3 weeks after delivery; therefore induction of lactogenic immunity is a most well-liked methodology of protection. Pups have been challenged 5 days after delivery and had been 80�100% protected compared to control pups, 100 percent of which developed diarrhea. Some early successes in the manufacturing of vaccine candidates in crops had been achieved with the event of recombinant rabies subunit vaccines in tomato, spinach, and tobacco (McGarvey et al. Oral immunogenicity and parenteral protective efficacy of those vaccines have been shown in mice. Rabies is a zoonotic illness affecting mammals worldwide, spread by bites of contaminated animals. In creating countries, rabies represents a particular health risk because of widespread infection in the stray canine population. In Latin America, another key reservoir of the rabies virus is the bat population that can unfold the illness to livestock. Sheep in different teams had been fed with a single dose of floor maize kernels containing 0. After challenge with a deadly dose of rabies virus, all vaccinated groups achieved survival charges of no much less than 50%, with the best dose of two. These outcomes show that a plant-produced subunit vaccine may be effective at protecting massive livestock animals in opposition to rabies. In addition to these virus vaccines, plants have additionally been investigated as vaccine production platforms to protect livestock from bacterial pathogens. Mannheimia haemolytica is among the main causal agents of pneumonic pasteurellosis in cattle, a disease with worldwide economic influence. Current treatment involves using antibiotics, however prevention with vaccines could be preferable. Porcine Vaccines Bacterial and parasitic illnesses, along with several viral illnesses, have also been focused by researchers investigating plants as manufacturing platforms for porcine vaccines. In 2012, researchers reported the oral efficacy of plantproduced vaccines in opposition to porcine cysticercosis (Betancourt et al. A vaccine consisting of three peptides has been produced in transgenic papaya callus (S3Pvac-papaya) (Hernandez et al. Rabbits received oral administration of 20 mg of callus, boosted on day 7, and have been challenged (with Taenia pisiformis, carefully associated to T. Upon sacrifice of the animals, researchers discovered a 90% reduction in hepatic lesions and 94% discount in cysticerci recovered, thereby showing efficient protection of rabbits (Betancourt et al. Another economically essential parasite of pigs, in addition to people and different warm-blooded animals and livestock, is T. The experiment showed induction of both systemic and mucosal immune responses and a 59% reduction in mind cyst load in comparability with that of a management. In addition to these parasitic diseases, the bacterial postweaning diarrhea brought on by enterotoxic E. The authors confirmed that the antigen could survive extended incubation in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids, indicating its stability within the gastrointestinal tract and suitability as an oral immunogen. Mucosal Vaccines from Plant Biotechnology Chapter 65 1283 Most of the porcine ailments presently targeted by plantbased vaccines are brought on by viruses. This illness, first acknowledged in 1987, has become some of the essential illness of farmed pigs in North America and Europe, and is becoming a problem in other components of the world, notably Asia. Other teams have just lately reported expression and immunogenicity of the nucleocapsid protein (N) produced in transgenic soybean (Vimolmangkang et al. Production of antigen in soybean and maize has the good thing about simple storage with out chilly chain; however, further experiments might be needed to show the efficacy of those vaccine candidates. Vaccines in opposition to other viral illnesses related to the swine business have been investigated for manufacturing in vegetation with limited success.
Primaquine 7.5 mg purchase fast delivery
Cold adaptation of parainfluenza virus sort 3: induction of three phenotypic markers symptoms lyme disease order primaquine 7.5 mg free shipping. The efficacy of live attenuated treatment diabetic neuropathy buy 15mg primaquine with amex, cold-adapted, trivalent, intranasal influenzavirus vaccine in children. Correlates of immune safety induced by live, attenuated, cold-adapted, trivalent, intranasal influenza virus vaccine. Evaluation of combined stay, attenuated respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza three virus vaccines in infants and young children. Phase 2 evaluation of parainfluenza type 3 cold passage mutant forty five stay attenuated vaccine in healthy youngsters 6�18 months old. The effect of the physical form of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) carriers on the humoral immune response to co-delivered antigen. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein expressed by attenuated vaccinia virus protectively immunizes mice. An outbreak of severe respiratory tract an infection as a outcome of human metapneumovirus in a long-term care facility. Positive selection ends in frequent reversible amino acid replacements in the G protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus. Parenteral influenza vaccination induces a fast systemic and local immune response. Subclass distribution and molecular type of immunoglobulin A hemagglutinin antibodies in sera and nasal secretions after experimental secondary infection with influenza A virus in humans. Contributions of the structural proteins of extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus to protecting immunity. Activation of cytokine genes in T cells throughout major and secondary murine influenza pneumonia. Transforming progress factor-beta: activation by neuraminidase and position in extremely pathogenic H5N1 influenza pathogenesis. Guidance for trade: scientific knowledge needed to help the licensure of seasonal inactivated influenza vaccines. Serologic response to commonplace inactivated influenza vaccine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected youngsters. Proinflammatory cytokine responses induced by influenza A (H5N1) viruses in major human alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells. Recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara expressing the spike glycoprotein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus induces protective neutralizing antibodies primarily targeting the receptor binding area. Seasonal influenza infection and live vaccine prime for a response to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 vaccine. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease Critical regulation of early Th17 cell differentiation by interleukin-1 signaling. Development and persistence of local and systemic antibody responses in adults given reside attenuated or inactivated influenza A virus vaccine. Serum and nasal wash antibodies associated with resistance to experimental problem with influenza A wild-type virus. Potent high-affinity antibodies for treatment and prophylaxis of respiratory syncytial virus derived from B cells of contaminated sufferers. Progress in understanding and controlling respiratory syncytial virus: still crazy in spite of everything these years. Observations of infections with and illness as a result of parainfluenza, mumps and respiratory syncytial viruses and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Heterosubtypic neutralizing antibodies are produced by people immunized with a seasonal influenza vaccine. A neutralizing antibody selected from plasma cells that binds to group 1 and group 2 influenza A hemagglutinins. An early humoral immune response in peripheral blood following parenteral inactivated influenza vaccination. Evaluation of a virosomal H5N1 vaccine formulated with Matrix M adjuvant in a part I scientific trial. Human metapneumovirus fusion protein vaccines which may be immunogenic and protective in cotton rats. The impact of co-administration of adjuvants with a nanoparticle-based genetic vaccine supply system on the resulting immune responses. Influenza virosomes are an efficient delivery system for respiratory syncytial virus-F antigen inducing humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Fatal consequence of human influenza A (H5N1) is related to excessive viral load and hypercytokinemia. A severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus that lacks the E gene is attenuated in vitro and in vivo. Lack of antibody affinity maturation due to poor Toll-like receptor stimulation leads to enhanced respiratory syncytial virus illness. Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery techniques of proteins and vaccines: a mechanistic strategy. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Progress in the improvement of respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus vaccines. A randomized managed trial of cold-adapted and inactivated vaccines for the prevention of influenza A illness. Systemic and mucosal immune responses in young children and adults after parenteral influenza vaccination. Correlation of laboratory studies with scientific responses to A/New Jersey influenza vaccines. Human infections with influenza A(H3N2) variant virus in the United States, 2011�2012. Prior H1N1 influenza an infection and susceptibility of Cleveland household examine individuals during the H2N2 pandemic of 1957: an experiment of nature. A prospective study of parainfluenza virus kind 4 infections in children attending daycare. Identification of a linear heparin binding area for human respiratory syncytial virus attachment glycoprotein G. Correlation of mobile immune responses with safety against culture-confirmed influenza virus in young children. A dilemma for mucosal vaccination: efficacy versus toxicity using enterotoxin-based adjuvants. A area trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Parainfluenza virus kind 3: seasonality and danger of infection and reinfection in young kids. Genetic predisposition to wheeze following respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Biological challenges and technological alternatives for respiratory syncytial virus vaccine development.
Buy discount primaquine 7.5 mg online
The inhibitory effect of C-reactive protein on bacterial phosphorylcholine platelet-activating factor receptor-mediated adherence is blocked by surfactant medicine 2 7.5 mg primaquine proven. Lipid A acylation and bacterial resistance against vertebrate antimicrobial peptides symptoms wheat allergy 15mg primaquine cheap otc. Susceptibility to Vibrio cholerae infection in a cohort of family contacts of sufferers with cholera in Bangladesh. Direct nucleation and bundling of actin by the SipC protein of invasive Salmonella. Serogroup-related escape of Yersinia enterocolitica YopE from degradation by the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are important for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. Effect of neuraminidase on the expression of the 3-fucosyl-N-acetyllactosamine antigen in human tissues. Immune privilege in the intestine: the establishment and maintenance of non-responsiveness to dietary antigens and commensal flora. Detection of the phosphorylcholine epitope in streptococci, Haemophilus and pathogenic Neisseriae by immunoblotting. The Vibrio cholerae ToxR/ TcpP/ToxT virulence cascade: distinct roles for two membranelocalized transcriptional activators on a single promoter. Regulation and temporal expression patterns of Vibrio cholerae virulence genes during infection. Surfactant proteinA binds group B streptococcus enhancing phagocytosis and clearance from lungs of surfactant protein-A-deficient mice. Role of neuraminidase in deadly synergism between influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Bacterial Interactions with Mucosal Epithelial Cells Chapter forty nine 971 McGuckin, M. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein alerts activation of adaptive immunity. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella Typhimurium virulence. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Actin-based motility is enough for bacterial membrane protrusion formation and host cell uptake. Attaching and effacing actions of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Airway hyperresponsiveness in transgenic mice overexpressing platelet activating factor receptor is mediated by an atropine-sensitive pathway. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase superfamily by a Yersinia effector. Disruption of signaling by Yersinia effector YopJ, a ubiquitin-like protein protease. The secreted IpaB and IpaC invasins and their cytoplasmic chaperone IpgC are required for intercellular dissemination of Shigella flexneri. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration promotes invasion of colonic epithelial monolayer by Shigella flexneri. Acute inflammation causes epithelial invasion and mucosal destruction in experimental shigellosis. The cell biology of Listeria monocytogenes an infection: the intersection of bacterial pathogenesis and cell-mediated immunity. Identification of a carbohydrate recognition area in filamentous hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. The contrasting mechanisms of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and group B Neisseria meningitidis. Genomewide affiliation examine identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in illness pathogenesis. Contribution of novel choline-binding proteins to adherence, colonization and immunogenicity of Streptococcus pneumoniae. The bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis encodes a transcriptional activator required for coordinate regulation of a number of virulence genes. Yersinia outer protein P of Yersinia enterocolitica concurrently blocks the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and exploits lipopolysaccharide signaling to trigger apoptosis in macrophages. The pneumococcal serine-rich repeat protein is an intra-species bacterial adhesin that promotes bacterial aggregation in vivo and in biofilms. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri inside HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. YopH prevents monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 expression in macrophages and T-cell proliferation via inactivation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Environmental alerts modulate ToxT-dependent virulence factor expression in Vibrio cholerae. Translocation of Yersinia entrocolitica throughout reconstituted intestinal epithelial monolayers is triggered by Yersinia invasin binding to beta1 integrins apically expressed on M-like cells. Co-evolution and exploitation of host cell signaling pathways by bacterial pathogens. Microbial patterns signaling through toll-like receptors 2 and 5 contribute to epithelial restore, growth and survival. Cellular senescence increases expression of bacterial ligands within the lungs and is positively correlated with increased susceptibility to pneumococcal pneumonia. Control of the ToxR virulence regulon in Vibrio cholerae by environmental stimuli. Peptidoglycan: a crucial activator of the mammalian immune system during an infection and homeostasis. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization issue coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Bacterial Interactions with Mucosal Epithelial Cells Chapter 49 973 Theivanthiran, B. Modulation of bacterial entry into epithelial cells by affiliation between vinculin and the Shigella IpaA invasin. IpaC induces actin polymerization and filopodia formation throughout Shigella entry into epithelial cells. Characterization of two adhesins of Bordetella pertussis for human ciliated respiratory-epithelial cells. Salmonella pathogenicity island 1-independent induction of apoptosis in contaminated macrophages by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. The Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein and human fibronectin bind to mutually unique sites on the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin receptor. Innate immunity turned inside-out: antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps. Toll-like receptor four mediates innate immune responses to Haemophilus influenzae infection in mouse lung. Role of M cells in initial antigen uptake and in ulcer formation within the rabbit intestinal loop mannequin of shigellosis.
Bluebonnet (Cornflower). Primaquine.
- Dosing considerations for Cornflower.
- How does Cornflower work?
- What is Cornflower?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Fever, menstrual disorders, yeast infections, constipation, coughs, liver and gallbladder disorders, eye irritation, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96426

Discount primaquine 7.5 mg overnight delivery
A hypothesis that drove a lot of the early work on plant-derived vaccines held that low-cost and orally delivered "edible" subunit vaccines could provide protection in opposition to infectious diseases in growing countries with limited medical infrastructures symptoms just before giving birth generic primaquine 7.5mg on line. A number of hurdles can intrude with the effectiveness of this method medications and grapefruit juice generic 15mg primaquine mastercard, including poor stability of proteins within the intestine, substantial variability of antigen content in plant tissues, and regulatory issues for the containment of transgenic crop plants and their use completely as pharmaceutical merchandise. These and different issues are mentioned in larger detail in other papers (Mason and Herbst-Kralovetz, 2012; Rybicki, 2009; Rybicki et al. Such challenges however, most workers and watchers of the field continue to see nice value in using vegetation for manufacturing of vaccine antigens. Importantly, compelling information on the protecting efficacy of orally delivered plant-derived vaccine antigens continue to accumulate, as discussed beneath intimately within the section on animal vaccines. The approaches for plant-based protein expression embody stably built-in transgenes into chromosomes in either the nucleus or the chloroplast, and transient expression utilizing vectors that may use plant virus replication components to amplify the transgene. We present solely a very brief dialogue here, and involved readers are referred to glorious current evaluation articles (Rybicki, 2010; Thuenemann et al. A plant expression vector, often a viral replicon, is constructed and mobilized into Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The Agrobacterium cultures are used for enormous infiltration of entire Nicotiana benthamiana plants in a large vacuum chamber. Tissue-specific promoters permit overseas proteins to accumulate in seeds (Nochi et al. Proteins that accumulate in seeds are very stable to temperature extremes and can be stored for months to years with little loss of protein activity. During the past decade, the use of speedy transient expression in vegetation (rather than the gradual manufacturing of plants with stably integrated transgenes) has elevated significantly and represents an ever-growing proportion of plant-based protein expression work. The growth of viral vectors has enabled very fast and really excessive ranges of protein expression in crops (Thuenemann et al. Protein expression levels at 1�2 mg per kilogram of leaf mass are often 10-fold higher than these obtained with stably transgenic plants, and point out the potential for purification of plant-produced proteins at costs that are economically competitive with microbial fermentation systems. The comfort of transient plant-based expression permits speedy response to rising viruses corresponding to influenza and norovirus, as described by Charles Arntzen in his tackle to the 238th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (Dylewski, 2009). We can even make the most of purified antigens for intranasal delivery, which requires more concentrated antigen at Mucosal Vaccines from Plant Biotechnology Chapter sixty five 1273 decrease doses than oral supply. Nasal immunization induced antigen-specific mucosal IgA responses in salivary glands, respiratory tract, intestines, and reproductive tracts in mammals (Harandi et al. Moreover, mucosal immunization can prime each mucosal and systemic immune responses (Kunkel and Butcher, 2002). We focus on studies that concerned humans or have shown strong indication of efficacy in preclinical research. Other than foundering or loss of power on the ship, a norovirus epidemic with projectile vomiting and protracted diarrhea have to be one of the disappointing vacations conceivable. Freeze-dried tissues of transgenic tomato fruit and potato tuber were fed to mice, with tomato proven to be a superior vehicle. Conversely, related doses of freeze-dried potato produced considerably poorer results, in all probability because of oxidation of phenolic compounds which are abundant in potato tuber. Since tomato fruit is low in phenolics, and high within the antioxidant ascorbic acid, such oxidation results have been minimal. Although the tomato delivery technique seemed "ripe" for further development, the winds of change were blowing and bringing quicker and extra sturdy transient expression systems. Murabutide is acknowledged by the nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 receptor on mammalian cells, and was accredited for testing in a quantity of medical trials as an injectable vaccine adjuvant. The latter might be improved by addition of gardiquimod adjuvant, but was still just like GelVac. After monumental makes an attempt over the past 30 years by researchers worldwide to develop a vaccine, the results to date are modest, at finest. A consensus of opinion among plant-based vaccinologists holds that mucosal immune responses are important, if not essential, to protecting efficacy, and thus typically give consideration to supply of antigens at mucosal websites. We will evaluate chosen works right here, and readers are directed to extra in depth review articles (Meyers et al. These workers generated steady transgenic tomato crops, and freeze-dried the fruits for oral supply to mice. Tomato powder was suspended in water and gavaged into mice at a dose of 30 ng antigen in 1 mL, thrice over a 4-week period. Ten days before ingesting the freeze-dried transgenic tobacco (eight doses over 2 weeks), the mice have been primed with a plasmid for expression of the identical fusion protein. The variety of mice in each group that seroconverted with antibody responses to gag protein (a) or gp41 (b) are plotted vs. These conflicting outcomes indicate that one must be very cautious when interpreting outcomes of feeding studies. A recent review article provides a very good survey of this area (Shchelkunov and Shchelkunova, 2010). Although neither of these studies used an adjuvant (unless one considers the chance that compounds found in either potato or lettuce could operate so), an attention-grabbing examine of oral immunogenicity in mice of alum-adsorbed yeast-derived vaccine at low doses over longer intervals confirmed efficient seroconversion (Kapusta et al. Immune tolerance is at all times a potential concern when antigens are delivered orally, and wishes additional research. Serum and fecal IgG and IgA correlated inversely with antigen dose, suggesting that oral tolerance occurred at higher doses. However, the comparatively poor antibody responses made the correlations considerably tenuous, and Tregs elevated considerably in mice immunized with wild-type tobacco. It appears probably that for human use, a purified preparation will be most popular, in order to precisely adjust the dosage to optimum ranges, and to keep away from possible and variable interfering results because of different components in crude samples. In this regard, high-level expression will facilitate purification, and the usage of a viral replicon system will profit these pursuits (Huang et al. We acknowledge that cooking the rice (or other edible plant material) could be very prone to denature the vaccine antigens, thus rendering them poorly immunogenic. In order to overcome this problem, Kiyono and coworkers are investigating the oral supply of rice flour derived from transgenic seeds. The MucoRice system has just lately attracted interest in its place method for the development of oral vaccines (Nochi et al. Rice seeds are edible tissues and capable of producing and storing comparatively large amounts of transgenic recombinant proteins (Boothe et al. Recombinant proteins expressed and accrued in rice seeds are stable for extended durations (Daniell et al. These novel traits of the rice seed protein expression and storage system can be utilized for the development of oral vaccine. Rice-Based Oral Vaccine (MucoRice) Attractiveness of Oral Vaccine for the Healthy Life the mucosal immune system is able to simultaneously executing two opposing immune responses together with lively. The MucoRice system is thus qualified as an appropriate system for the expression, accumulation, and storage of vaccine antigens. To demonstrate the versatility of the MucoRice system, the other toxin-related antigen, a nontoxic fragment of the C-terminal half of the heavy chain from botulinum neurotoxin sort A (BoHc), was expressed and produced by the seeds of MucoRice and induced neutralizing antigenspecific antibody responses in mice orally immunized with MucoRice-BoHc (Yuki et al. Further, the rice-based vaccine improvement was extended to the expression of virus-associated antigens.
Primaquine 15mg order without a prescription
Further shinee symptoms mp3 primaquine 15mg buy on-line, a number of licensed vaccines for ailments that initiate at mucosal surfaces are parenterally administered and provide robust safety Table 2) symptoms bowel obstruction 7.5 mg primaquine cheap amex. Monovalent sorts 1 + three bivalent vaccine recently licensed for use in growing countries Rotavirus-monovalent stay attenuated human rotavirus and multivalent animal/human reassortant rotavirus Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi-live attenuated S. A variety of licensed mucosal vaccines are delivered by way of the oral route, together with polio, rotavirus, cholera, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Intranasal vaccination acts by stimulating immune responses in the nasal-associated lymphoid tissue and can induce each systemic and mucosal immunity within the gut and the respiratory and genital tracts (Brandtzaeg, 2011; Jabbal-Gill, 2010). The giant intestine incorporates immune structures that can function inductive websites for mucosal immune responses. Further, this immunization technique induced more potent vaginal safety than following nasal or pores and skin vaccination. Overall, these research indicate that a variety of routes could be utilized to induce local mucosal immunity and safety; nevertheless, to date, solely oral and intranasal routes have been used for licensed human vaccines (Czerkinsky and Holmgren, 2012; Lycke, 2012). Currently quite lots of attenuated poxviral vaccine vectors are available, together with vectors with a demonstrated security record in humans (Liu, 2010). Notably, in depth use of smallpox vaccine has supplied a transparent understanding of its safety profile; these viruses have giant transgene capacity (up to 25 kbp) (Smith and Moss, 1983); broad tropism for varied cells, quick period of antigen manufacturing (like acute infection); expression of antigen in the cytoplasm. Also poxvirus production processes are compliant with good manufacturing practices and have an excellent safety observe record of recombinant poxviruses in people. It proved successful in generating sufficient immunity within the wild by way of the oral route to curtail rabies outbreaks in numerous species. Indeed, this demonstrates the advantages of an ideal vector; namely, it proved efficient. Even given the imprecise dosing within the wild, it was safe and simply delivered via the oral (mucosal) route. It was additionally assessed as a smallpox vaccine in over 150,000 recipients in Germany together with immunocompromised people without vital opposed results (McCurdy et al. The second immune correlate evaluation showed that prime titer anti-Env IgA antibodies instantly correlated with infection threat (Haynes et al. Clearly the level and length of protection afforded by this prime-boost regimen were marginal. A major concern with the utilization of Ad5-based vectors in people is preexisting immunity both from pure infection or from prior exposure to rAd5 (Quirk et al. The first recombinant Ad vectors generated had a capability for an 8 kb insert, whereas later generations may accommodate as much as 35 kb. Replacement of the early area 1 or, sometimes, the early region four of the viral genome with a transgene ends in replication-defective recombinant viruses. Human kind 5 Ad (AdHu5) is a typical explanation for acute higher respiratory tract an infection, i. More just lately, the potential use of human Ad5 as a recombinant vaccine vector has been widely explored. Indeed, recombinant Ads have been used to deliver vaccine antigens in over 90 preclinical and medical trials (Rollier et al. Randomization was prestratified by study site, gender, and baseline anti-Ad5 titer. The Step research was terminated in 2007 on the first information and safety monitoring board evaluate for futility. Based on these findings, a second section 2b efficacy trial performed in South Africa referred to as Phambili was additionally terminated. In distinction to the Merck rAd5, the Ad5 used right here had three genes deleted from the vector. Unfortunately, all these studies have been carried out using peripheral blood lymphocytes. In mild of the results of the Step trial and concern with security risks, the authors of the trial concluded, "Given our outcomes, it appears prudent to avoid using Ad5-vectored vaccines in populations of uncircumcised or Ad5 seropositive men until more data turn into out there" (Duerr et al. Criticism of this conclusion has been raised noting that the development towards increased acquisition of infection in baseline seropositive vaccinees was not statistically vital (Barouch, 2010; Buchbinder et al. Importantly, though, what has not been recognized and appreciated is that rAd vectors, together with Ad5, are usually tropic for mucosa sites and have been shown to be more potent following mucosal delivery. Indeed, for the reason that Seventies, licensed oral human Ad4 and Ad7 vaccines had been safely and effectively administered to hundreds of thousands of United States navy recruits by way of oral supply of lyophilized wild-type virus in gelatin-coated capsules to shield the virus from low pH of the abdomen (Quirk et al. Following oral administration, the virus replicates within the intestine asymptomatically. Delivery of a single oral dose generated an immune response that proved 95% effective in stopping Ad4 and Ad7-induced acute respiratory infections in more than forty,000 soldiers (Schwartz et al. Importantly, the route of immunization profoundly influences the geographical location of pathogen-specific T cells, the character of native humoral immune responses, and the longevity of immune memory; in turn, these determine the immune protective consequence following infections. These are being referred to as "uncommon serotype adenoviral vectors" and include human Ad11, Ad24, Ad26, Ad34, Ad35, and Ad48 in addition to simian adenoviruses, which are rarely neutralized in humans. Twenty-six isolates of ChAd-gag vectors had been screened for immunological potency by dose�response and ranked. Subsequently, two of the most potent ChAd isolates, ChAd3 and ChAd63, had been selected as vectors for medical development towards hepatitis C virus and Plasmodium falciparum malaria, respectively. Immunization of human volunteers with ChAd3 and ChAd63 induced potent T cell immunity in 100 percent of participants. Indeed, the ChAd-induced T cell responses have been among the highest ever observed in people with a single nonreplicating genetic vaccine vector (Colloca et al. In a follow-up research, it was found that Ad26EnvA elicited a broad range of humoral and cell-mediated responses in people (Barouch et al. Differences in reminiscence T cell responses elicited by Ad5 in comparison with Ad26, Ad35, and Ad48 were additionally demonstrated using these Ad vectors expressing lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus glycoprotein (Penaloza-MacMaster et al. Although Ad5 induced high levels of memory T cells, they exhibited practical exhaustion and decreased anamnestic potential following secondary antigen challenge in comparison with Ad26, Ad35, and Ad48 vectors. Rare serotype Ad vectors are in various levels of vaccine growth for malaria, tuberculosis, hepatitis C, and filoviruses (Michael, 2012). Additionally, prime-boost vaccination methods using rare serotype Ad vectors have shown promise (Liu et al. Half of the vaccinated macaques also received a boost with a mixture of all three vectors. In distinction, four of the vaccinated macaques have been protected against progressive infection. Thus, they could not arrive at the website of infection in a fast sufficient time frame to effectively limit mucosal and systemic spread of rapidly replicating viruses. These results have been subsequently confirmed and prolonged in a further study (Hansen et al. However, throughout this course of it encounters a plethora of antigens and potentially pathogenic microorganisms. The lung could be divided into three major compartments: the airway lumen, the lung interstitium, and the lung vasculature. The presence of ample anastomoses between the bronchial and the pulmonary circulations directs quite some systemic blood circulate into the pulmonary circulation (Doerschuk, 2000; Mitzner et al. Furthermore, compared to different mucosal websites, the pulmonary circulation and interstitium lure extra circulating T cells due to the truth that the lymph in the thoracic duct containing antigen (Ag)-experienced T cells from the regional lymphoid tissues empties first into the proper cardiac chambers and then instantly enters the pulmonary artery (circulation) (Jeyanathan et al.

Primaquine 15 mg generic free shipping
Lastly medicine vs dentistry order primaquine 7.5mg on line, manipulating genital immune responses to enhance Th1 or Th2 type responses is an unexplored research area treatment 2011 buy primaquine 7.5mg with amex. These infections occur most commonly in suckling animals or in poultry underneath three weeks of age, but may be widespread postweaning and in prone seronegative or confused adult animals (Saif and Jackwood, 1990). Induction of local secretory IgA (S-IgA) antibodies (prevent attachment, invasion, and neutralize toxins or infectious agent) and mucosal cellular immune responses (against intracellular micro organism and viruses) by vaccines are important for cover from enteric pathogens. Cryptopatches or clusters of lymphoid cells in the basal lamina propria happen in mice, but are absent in pigs (Pabst et al. These differences in immune components suggest that vaccine studies carried out in mice may fail to translate to domestic animals or people. Enteric pathogens have completely different characteristics related to their intestinal tropism and replication, requiring totally different vaccination methods. Enteric viruses have predilections for replication in distinct vertical and longitudinal regions of the small or giant intestines. Cytolytic an infection of enterocytes results in various levels of villous loss and fusion, decreased small intestinal absorptive capability, and a malabsorptive, maldigestive diarrhea (Saif, 1999a). Thus, viral diarrheas could be of variable severity and act via multiple mechanisms that differ from those of enteric bacteria, most of which trigger secretory diarrhea mediated by enterotoxins (Fairbrother and Gyles, 2006). The enteropathogenicity of bacteria is decided by their virulence factors including adhesion elements (fimbriae or pili) and enterotoxins; therefore, bacterial vaccines usually must prevent attachment and toxin motion inside the intestine (Fairbrother and Gyles, 2006). Vaccines to Induce Passive and Active Immunity to Type I Enteric Viruses Infecting Villous Enterocytes in Neonates Passive Immunity Neonates may be shielded from enteric infections by offering passive lactogenic immunity, which can be achieved by immunizing mothers preparturition. Active Immunity Rotavirus is a significant cause of dehydrating diarrhea in younger livestock, infants, and poultry (Saif and Fernandez, 1996). Although a significant reduction in morbidity and mortality was noticed in a area trial among vaccinated calves, in the majority of herds (compared to earlier years), subsequent area studies revealed variable efficacy. Experimental studies suggested that maternal antibodies interfered with live oral vaccine replication and suppressed development of lively immunity (Saif and Fernandez, 1996). These findings recommend that higher protection charges are associated with early proinflammatory and Th1 cytokine responses, which promote cytotoxic T cell exercise and viral clearance, and later Th2 induced cytokines, which are essential for protecting S-IgA antibody responses. Studies have shown that immunogenicity and efficacy of mucosal vaccines may be improved by the use of appropriate strains of probiotics that modulate mucosal and systemic immune responses, by interaction with epithelial cells and the underlying intestinal immune cells (Fukushima et al. Further efficacy checks in pups with maternal antibodies are needed to assess their industrial potential. F4 (K88) and F18 are the major fimbrial adhesins current on swine enterotoxigenic E. Recent vaccine research have centered on administration of purified bacterial subunits (transgenically expressed adhesin of F4 fimbriae in plants) and mucosal adjuvants (Verdonck et al. Summary Studies of live oral enteric vaccines in animals have clarified the mechanisms of induction of protective immunity towards enteric illness and contributed to our understanding of the frequent mucosal immune system. However, business stay oral vaccines typically have shown insufficient or inconsistent efficacy beneath field circumstances (Saif and Jackwood, 1990; Saif and Fernandez, 1996). Major obstacles to improved efficacy of oral vaccines embody: (1) maternal antibodies in the gut of neonates (mainly colostrum and milk antibodies), which intrude with live vaccine replication; (2) qualitative and quantitative limitations in the neonatal immune system, although neonates are immunocompetent; (3) the inability of attenuated vaccine strains to adequately infect (too excessive attenuation) or stimulate S-IgA antibodies within the intestine; (4) the use of inappropriate (or unstable) antigens or route for subunit vaccines; (5) the lack of oral delivery automobiles or mucosal adjuvants for subunit vaccines; and (6) infection by pathogens prior to vaccination. To develop effective mucosal vaccines, you will want to determine correlates of protection in opposition to enteric pathogens. Generally for localized gut infections, S-IgA antibodies and intestinal T cells play an necessary function. Improved vaccines that induce excessive levels of intestinal IgA antibodies in opposition to the suitable microbial antigens could be achieved by choosing the right vaccine formulation and delivery method. Vaccines also needs to induce: (1) heterotypic protection; (2) active immunity in the presence of maternal antibodies; and, (3) long-lasting immunological reminiscence. Maternal immunologic switch provides a crucial (though temporary) assist to survival for neonates. The enhancement of passive immunity by way of vaccination of the mother has been a successful disease prevention strategy in domesticated animals. Vaccinated mothers develop larger ranges of particular antibodies in colostrum and milk and elevated ranges of immunity of their offspring (Glezen, 2001; Saif and Fernandez, 1996). Passive immunity can also be enhanced by oral administration of immune milk or heterologous antibody preparations. Immunoglobulins of the IgG2 and IgG3 isotypes of camelids consist of heavy chains with out related gentle chains (Hamers-Casterman et al. Unfortunately, passive antibodies often intervene with lively immunization of young animals and birds. Various vaccination methods have been developed to reduce the suppressive effects of maternal antibodies, however improved adjuvants and antigen-delivery systems are wanted to facilitate efficient induction of lively immunity in the presence of maternal antibodies. This section will handle past, present, and future approaches for enhancing passive immunity in veterinary species. Colostrum dietary supplements, colostrum replacers, and plasma products have been developed commercially to handle this problem, with variable success. Vaccination of the dam in late pregnancy can enhance antibody titers in colostrum and after suckling in the serum of the offspring (Saif and Fernandez, 1996). The advantages of vaccination of the dam for enhancing passive immunity could be lost if colostrum is of low high quality or if absorption of colostral Ig is inefficient. Transfer of Maternal Immunity the transfer of systemic passive immunity from mom to offspring can happen prenatally, via the placenta or yolk sac, or postnasally via ingestion of colostrum and milk, relying on the species. In avian species IgY, the functional equal of mammalian IgG, is transferred to the yolk to passively defend the growing chick (Kovacs-Nolan and Mine, 2012). In primates and rabbits, maternal IgG is transferred across the placenta to the fetus. In rodents, transplacental switch occurs together with extended (16�21 days) postnatal transfer by the use of colostrum and milk (Husband, 1998). In dogs and cats transfer of IgG happens by a mix of prenatal and postnatal mechanisms, with 5% to 10% of total transfer occurring earlier than birth (Tizard, 2013). In ruminants, horses, and pigs, offspring are born virtually agammaglobulinemic and transmission of Ig occurs only through colostrum for a restricted time after birth (Tizard, 2013). After the transition from manufacturing of colostrum to milk, Ig are no longer absorbed from the intestines and only act locally in the gastrointestinal tract. Immunoglobulin absorption in neonates of huge domestic species is facilitated by the presence of protease inhibitors in colostrum and its efficiency declines rapidly after delivery, with maximal absorption occurring within the first four h. The cessation of absorption of intact macromolecules is termed "intestine closure," and occurs at totally different ages in numerous species. Mechanisms of Clearance of Passively Acquired IgG the half-life of Ig varies significantly among species of home animals and with the Ig isotype. Neonatal receptor for Fc of IgG (FcRn) is involved in homeostasis of serum ranges of IgG normally, but distinct mechanisms might operate in neonates. The major route of clearance of passively acquired maternal IgG1 in calves is transfer from the serum to the intestine (Besser et al. If titers of passive circulating antibodies are excessive enough, the transfer of antibodies from the circulation to the intestinal lumen can mediate short-term protection towards rotavirus diarrhea (Besser et al. The same mechanism could additionally be practical in piglets (Saif and Wesley, 1999; Parre�o et al.
Primaquine 7.5 mg buy discount online
Fifty p.c of students and teachers were affected 92507 treatment code 15 mg primaquine generic with mastercard, and there was a 32% secondary attack rate among relations of main circumstances medications 2016 primaquine 15mg purchase with visa. Fecal filtrates collected from ill people related to the outbreak have been used to experimentally infect grownup volunteers (Dolin et al. The agent was named the Norwalk virus after the site of the preliminary outbreak, and it turned the prototype pressure within the Norovirus genus. A variety of different small spherical viruses have been subsequently recognized in association with outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in a variety of scientific settings. Progress in understanding NoVs was slowed due to the lack to propagate the virus in vitro until the genome of the Norwalk virus was cloned and sequenced within the early Nineties (Jiang et al. This breakthrough led to the event of more delicate diagnostic assays, including strategies for detecting the viral genome, capsid protein, and antibody responses to the virus (Atmar and Estes, 2001). Distinct strains that had been suspected on the idea of experimental human infection research were confirmed by genomic sequencing (Glass et al. SaVs were first described in association with an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis that occurred in an toddler residence in Japan in 1979 (Chiba et al. Electron microscopy revealed virus particles with a "Star-of-David" configuration. NoVs are estimated to trigger 21 million cases of acute gastroenteritis and as a lot as 10% of hospitalizations for gastroenteritis in the United States annually (Lopman et al. It may be the second main cause of gastroenteritis-associated death in the United States, primarily in the aged (Hall et al. In addition, it causes significant morbidity and health-care costs, with an estimated 400,000 emergency department visits and 1. The impact of SaVs has been much smaller (<10% of NoVs) and extra restricted to the extremes of age (<5 years or >65 years) in prevalence studies of acute gastroenteritis (Hall et al. NoVs are the most typical explanation for both endemic and epidemic gastroenteritis (Atmar and Estes, 2006). Outbreaks occur in a selection of settings, however especially in semiclosed populations, including colleges, recreational camps, cruise and navy ships, hospitals, and nursing houses. Some human strains will grow in gnotobiotic pigs and calves and in nonhuman primates (Cheetham et al. The human infectious dose 50% has been estimated to be as low as 18 virions (Teunis et al. SaVs are additionally unfold via fecaloral spread and are often foodborne pathogens. NoVs and SaVs are divided into genogroups based upon sequence analyses of their genomes. Both NoVs and SaVs bear recombination primarily based upon analyses of the sequences of nonstructural and structural proteins. The recombination occasions could lead to changes in the evolutionary price of the virus, rising variety and flexibility (Mahar et al. Electron microscopy identifies the virus in fecal samples from less than half of infected persons (Atmar and Estes, 2001). Antigen detection strategies have also been developed, but commercially available assays also have poor sensitivity, with their greatest applicability being within the evaluation of outbreaks, where multiple fecal samples could be assayed (Duizer et al. Clinical Illness and Mechanisms of Pathogenesis Both NoVs and SaVs trigger acute gastroenteritis characterized by a combination of the next signs: nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Longer symptom length has been noticed in young youngsters (median of 6 days for less than 1 12 months of age) and in hospitalized patients (median of three days) (Lopman et al. Immunocompromised sufferers, together with stem cell and strong organ transplant recipients, can have symptomatic infection for months or even years (Roddie et al. A comparison of SaV and NoV diseases in Finnish youngsters between 2 months and 2 years of age recognized more severe vomiting in NoV infections and more extreme diarrhea in SaV infections; overall, NoVs brought on extra severe gastroenteritis in this age group than SaVs (Pang et al. The commonest complication of NoV infection is quantity depletion, and this can be further complicated by electrolyte abnormalities. Therapy is oral or intravenous fluid repletion with electrolyte supplementation as wanted. Early human experimental an infection research advised that some individuals are genetically resistant to NoV an infection (Parrino et al. These glycans are expressed on the surface of the intestinal mucosa and appear to serve as attachment components for virus binding to the gut epithelium (Marionneau et al. Glycan specificity varies among genotypes such that nearly all persons ought to be prone to a minimal of some NoV genotypes (Huang et al. The pathogenetic mechanisms responsible for the disease manifestations are unknown right now. Histopathological modifications occur within the proximal small intestine of persons symptomatically contaminated with NoVs however not within the gastric fundus, antrum, or in colonic mucosa. In addition, the lamina propria is infiltrated with polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cells, and the intestinal epithelium is vacuolated. These adjustments may last as lengthy as four days following resolution of signs, however then the histology returns to regular. The brush border enzyme exercise in the small intestine also decreases and results in steatorrhea and delicate carbohydrate malabsorption (Agus et al. However, fecal virus shedding can remain at excessive levels for every week or extra after the resolution of signs, and low ranges of the virus can be noticed for up to 8 weeks in otherwise wholesome adults (Atmar et al. Viral Acute Gastroenteritis Chapter 57 1093 Immunity the inability to propagate NoVs in vitro has hampered the study of viral immunity due, partially, to the shortcoming to perform neutralization assays. Similar results are obtained when this blocking exercise is measured in a hemagglutination assay (Czako et al. IgG and IgA responses are commonest, though IgM responses additionally happen within the majority of contaminated adults (Gray et al. Heterotypic serological responses to NoVs from different genotypes can be measured, though the frequency and magnitude of such responses are decrease. The heterotypic responses are often IgG; IgA and IgM heterotypic responses happen infrequently (Treanor et al. Salivary IgG and IgA immune responses also could be measured in most contaminated individuals. Similar to responses seen within the serum, salivary IgA ranges peak earlier than salivary IgG levels (Moe et al. Few data can be found on changes in fecal IgA antibody ranges, though in a single challenge study, prechallenge virus-specific fecal IgA levels were larger in those who became infected, compared to ranges in uninfected persons (Okhuysen et al. Mucosal antibody responses in saliva, fecal, vaginal, and semen samples had been noticed in lower than half of the vaccinees. Humoral immune responses had been additionally observed in individuals consuming transgenic potatoes expressing the NoVs capsid antigen.
